Voice of the Sea, Innovation in Science Communication – Professor Kanesa Duncan Seraphin, University of Hawai’i at Mānoa
Original Article Reference
https://doi.org/10.26320/SCIENTIA292
Share Episode
About this episode
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. 
What does this mean?
Share: You can copy and redistribute the material in any medium
or format
Adapt: You can change, and build upon the material for any
purpose, even commercially.
Credit: You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the
license, and indicate if changes were made.
Related episodes
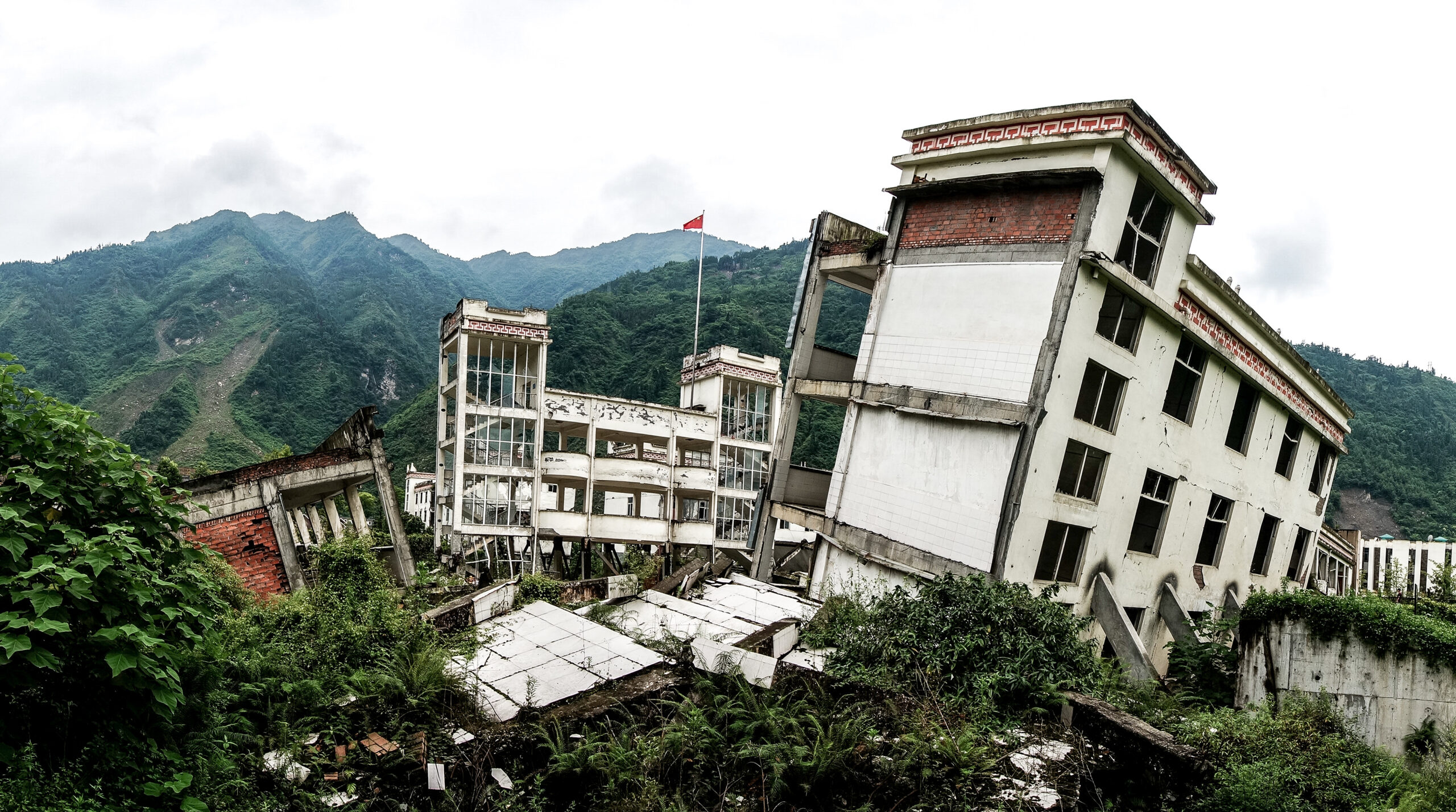
Dr. Zhe Su | Understanding the twisted tectonics of the Sichuan basin
The Sichuan basin in southern China is a region of deep geological and seismological complexity, which has so far prevented researchers from understanding its tectonic past. Through fresh analysis of previous observations, combined with the latest modelling techniques, a team led by Dr. Zhe Su at the National Institute of Natural Hazards, Beijing, suggests for the first time that the entire Sichuan basin is slowly rotating. Their result could explain the origins of one of the deadliest earthquakes in living memory, and could also help seismologists to better predict when earthquakes will strike the region in the future.
Dr. Claudia Ituarte-Lima – Dr. Radu Mares | How Latin America’s Groundbreaking Treaty Intersects with European Economic Law
Research by Dr. Claudia Ituarte-Lima and Dr. Radu Mares at Lund University examines how a pioneering environmental agreement in Latin America and the Caribbean introduces new ways of protecting nature and human rights. Their study reveals both opportunities and challenges in how this regional treaty interacts with European Union trade laws, offering insights into how different regions can work together to protect the environment and strengthen democracy.
Dr. Allen Place | Small but Deadly: The Tale of K. veneficum
The oceans, huge and brimming with diverse lifeforms, pose no less a struggle for survival for their inhabitants than that faced by creatures on dry land. Evolution has furnished marine organisms with huge array of defensive, and indeed, offensive adaptations to help them to thrive in this battleground. Among the organisms who live and compete in the ocean are dinoflagellates. These are small, single-celled creatures that are an important component of plankton found in marine ecosystems. Despite their tiny size, dinoflagellates such as Karlodinium veneficum can wield potent biochemical weaponry that gives them an edge against other competing organisms. Decades since the discovery of the toxic properties of Karlodinium veneficum, researchers such as Dr. Allen Place of the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Sciences, and his colleagues, have begun to unravel the secrets of its potent toxins, called karlotoxins. Their findings offer fascinating insights into the interactions of marine life and the weapons they adopt to capture prey and deter predators.
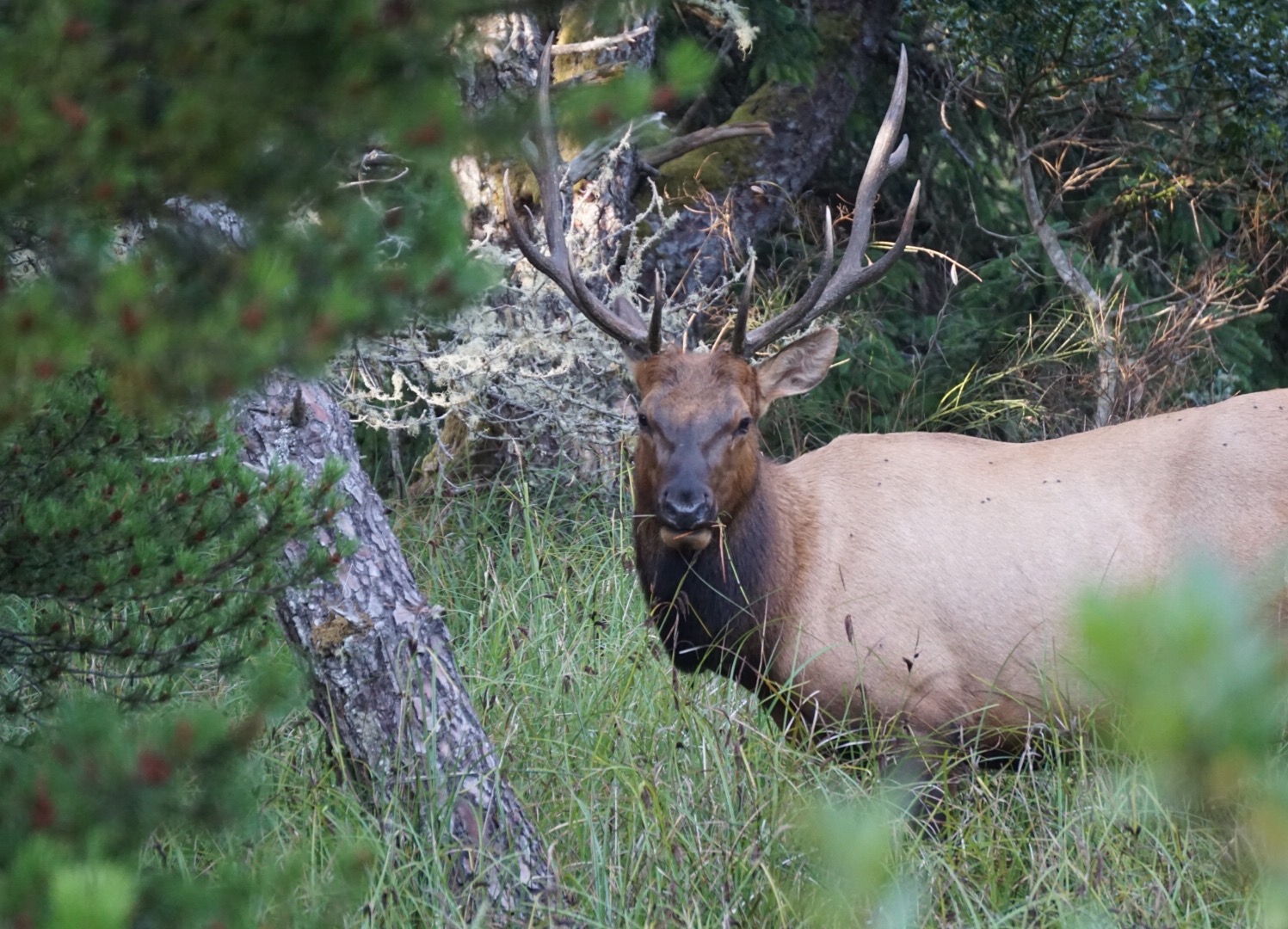
Dr. Andrea Grindeland | The Tiny Heroes That Could Save Deer and Elk from Chronic Wasting Disease
It’s not difficult to picture a lush forest landscape populated with majestic deer and elk, long admired for their prowess and strength. Now, imagine that same scene, but instead of healthy and happy animals browsing a forest ecosystem, we see creatures that are thin and disoriented, that struggle to run or even stand, with halting and confused movements that are pitiable and distressing to watch. This is the harsh reality of Chronic Wasting Disease, an illness that currently has no cure and that threatens such wildlife around the world. Part of the challenge with Chronic Wasting Disease is the difficulty in studying it reliably in wildlife. The disease has subtle signs at an early stage, and it is difficult to obtain robust and reproducible data from large, wild animals who often live in remote and poorly accessible forest ecosystems. Consequently, researchers have turned to an unlikely but powerful ally, the tiny laboratory mouse, to model and study the disease under laboratory conditions. Dr. Andrea Grindeland of the McLaughlin Research Institute, and her colleagues, have authored a review of the existing mouse models of Chronic Wasting Disease. These tiny creatures have been engineered to mimic the biology of cervids, such as deer and elk, and are providing crucial insights into how Chronic Wasting Disease evolves, is transmitted, and how it might one day be controlled or even eradicated.
Increase the impact of your research
• Good science communication encourages everyday people to be scientifically literate so that they can analyse the integrity and legitimacy of information.
• Good science communication encourages people into STEM-related fields of study and employment.
• Good public science communication fosters a community around research that includes both members of the public, policymakers and scientists.
• In a recent survey, 75% of people suggested they would prefer to listen to an interesting story than read it.

Upload your science paper
Step 2
SciPod script written
Step 3
Voice audio recorded
Step 4
SciPod published