Health and Medicine
Explore Health and Medicine
Dr. Qiang Wang | Fishing for Findings: Uncovering the Genetics of Hearing Loss
Our hearing is amongst our most profound senses, connecting us to the surrounding world through sound. However, this connection is diminished or absent altogether in millions of people around the world because of hearing loss. Hearing loss is a common sensory disorder and is often hereditary. The condition can be caused by complex genetic factors, and so far, researchers have linked over 150 genes to hearing impairment. Now, a new collaborative study led by Dr. Qiang Wang of the South China University of Technology, Dr. Tao Cai from the National Institute of Health, and Dr. Yuan Li from the China-Japan Friendship Hospital in Beijing, has uncovered a new genetic clue, a mutation in the OXR1 gene, that could upend our understanding of hereditary hearing loss, and the eventual treatments that we develop to combat it.

Dr. Sarallah Rezazadeh | Unlocking the Secrets of Aging: How Stem Cells Hold the Key to Vitality
Aging is a tale written by the cells in our bodies, although some cell types play a bigger role than others. At the crux of this story is an intriguing protagonist: the stem cell. These master builders, which can differentiate into any cell type, thereby helping to replace diseased or worn-out tissues, are essential for tissue repair and in maintaining health into old age. But as we get older, the capabilities of stem cells gradually diminish, which is known as stem cell exhaustion and is a key facet of aging itself. Stem cell exhaustion plays a role in a large number of age-related diseases, meaning that it could be a crucial research target in developing new treatments and techniques to help us age well. A Research Topic in the open-access journal Frontiers in Aging has been curated by Dr. Sarallah Rezazadeh of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and Professor Georgina May Ellison-Hughes of King’s College London. The Topic collects groundbreaking studies into stem cell exhaustion under one open-access roof, exploring the detailed mechanisms underlying the phenomenon and establishing the field in a wider context to identify promising therapeutic approaches for those later in life.
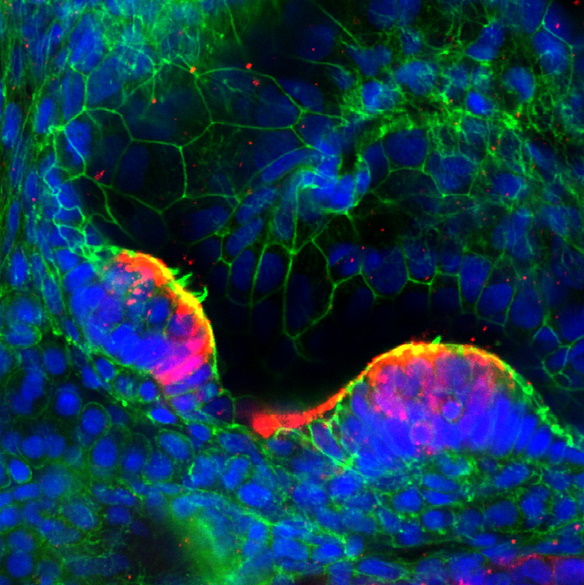
Dr. Mingjun Xie | A Blueprint for Life: Creating Blood Vessels in Bioprinted Tissues
A future where injured or diseased organs can be removed and replaced with new lab-printed tissues that are customized specifically for each patient is not as far away as you might think. These functional and living tissues could grow naturally within the body, and repair and sustain themselves over time. While these concepts were once in the realm of science fiction, advances in bioprinting, which is a form of 3D printing using biological “inks” (known as bioinks) loaded with living cells, are bringing them closer to reality. Among the researchers advancing this field is Dr. Mingjun Xie of Zhejiang University, China, and colleagues, who are performing work that addresses a significant challenge in bioprinting. This involves creating large portions of tissues that have a functional vasculature, thereby mimicking the complexity of native tissues and organs.

Prof. Eugenio Cersosimo | Cardio-Renal Protection and Blood Sugar Balance: How SGLT-2 Inhibitors Are Changing Diabetes Care
In their ongoing quest to improve diabetes management, researchers are searching for new insights into the mechanisms through which the body manages blood sugar levels. Prof. Eugenio Cersosimo and colleagues at the University of Texas Health Science Center recently reported a breakthrough that could change how we understand glucose control and increase our ability to manage type 2 diabetes. Their study examines two medications, dapagliflozin, an SGLT-2 inhibitor, and exenatide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, and how they can work together to control blood sugar levels by exploiting a previously unknown kidney-to-liver signalling pathway. Their findings have unravelled some important underlying mechanisms that provide strong support for the cardio-renal protective effects reported in many large clinical trials with the use of SGLT-2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes. The demonstration that the kidney plays a central role in glucose regulation during exposure to SGLT-2 inhibitors represents a major advance in our understanding of diabetes treatment and the prevention of severe cardiovascular and renal complications.
Charles Frison-Roche | The Hidden Architects of Movement: The Role of MBNL Proteins in Movement
Researchers have made a significant advancement in understanding an important component of the nervous system: the neuromuscular junction, a crucial connection between nerves and muscles. A recent study performed by Charles Frison-Roche of the Center of Research in Myology in the Sorbonne University, Paris, and colleagues, reveals the role of proteins known as Muscleblind-like proteins, or MBNL proteins for short, which help to regulate motor coordination by helping to maintain neuromuscular junction stability. This discovery is potentially very useful, as loss-of-function of MBNL proteins is a hallmark of a genetic condition called Myotonic Dystrophy type 1 (or DM1 for short). DM1 disrupts muscle control, leading to muscle weakness, problems with balance, and other symptoms that can get progressively worse over time. MBNL proteins, and their role in the neuromuscular junction, may represent new treatment targets in DM1.

Unmasking a Silent Killer: How the LiverRisk Score is Changing the Rules of Liver Disease Detection
Liver disease is a significant health challenge globally. It can often progress unnoticed for years until it becomes life-threatening. Cirrhosis is the final stage of chronic liver diseases, and it can be caused by conditions such as viral hepatitis, excessive alcohol consumption, or metabolic-associated steatotic liver disease, which is linked to conditions such as obesity or diabetes. Once cirrhosis has set in, the tissue in the liver becomes permanently scarred, reducing its function, and this can progress to liver failure or liver cancer. Often, these conditions are not diagnosed in sufficient time for effective treatment. Happily, a new risk assessment tool called the LiverRisk score, developed by the LiverScreen Consortium, could pave the way for early liver disease diagnosis, potentially allowing clinicians to intervene before irreversible liver damage occurs. The LiverRisk score helps to identify those who are at risk of severe liver complications in the future. The diagnostic tool is designed to be easy to use, and is based on clinical markers that are widely available from routine blood tests.
Dr. Serena Kuang | Inside the Kidney’s ‘Countercurrent’ Mystery: A New Model for Teaching and Studying Water Balance
Our kidneys filter blood to remove waste and can regulate water balance. We’ve all experienced that when we’re thirsty urine becomes concentrated, signalling us to drink more water. When we drink excess water, we urinate more frequently, and the urine is diluted. The kidneys’ ability to concentrate or dilute urine according to our body’s need relies on countercurrent multiplication (or CCM), a complex process that generates a salt concentration gradient in the kidney. However, CCM is challenging to teach and understand. Dr. Serena Kuang, a researcher and educator at Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine, has developed a more understandable CCM model and clears up errors in existing explanations making CCM easier to understand and teach.
Dr Neil Cunnigham | The Heart of the Matter: How Simulation Reflects Clinical Stress in Critical Care Training
In the high-stakes world of critical care, medical professionals are frequently called upon to perform life-saving procedures under intense pressure. Among these, airway intubation stands out as one of the most critical and technically demanding tasks. This procedure, which involves inserting a tube into a patient’s airway to ensure that they can breathe, is often performed in emergency situations where seconds count. The ability to intubate swiftly and accurately can mean the difference between life and death. However, this task is also fraught with stress, particularly for trainees who are still developing their skills. To better understand how these trainees cope with the stress of intubation, Dr Neil Cunningham of the University of Melbourne and colleagues conducted a groundbreaking study comparing physiological stress responses in simulated and clinical environments. Their findings offer valuable insights into the effectiveness of simulation-based training, which has become a cornerstone of medical education.

Dr. Ivy Razmus | Reducing Pressure Injuries in Hospitalized Children and Babies
The development of pressure injuries in hospital patients is a regular occurrence, and certain areas of the body are more susceptible. Although there is abundant research on pressure injuries in adult patients, studies relating to infant and child patients are lacking. Dr. Ivy Razmus at the University of Detroit Mercy has conducted extensive research on the prevention of pressure injuries in patients under the age of 12 years. She highlights the crucial role of advanced practice nurses in managing this widespread problem.

Pulque: The Ancient Drink That Could Shape the Future of Health
Pulque, an ancient Mexican beverage, is making waves in the scientific community—not just as a cultural relic, but as a potential health-boosting powerhouse. A team of researchers, including Prof. Rogelio Valadez-Blanco, Dr. Yesica Ruiz-Ramírez, and Prof. Paula Guadarrama-Mendoza, from Universidad Tecnológica de La Mixteca, has been investigating the hidden potential of the bacteria found in this traditional drink. Their findings suggest that pulque’s naturally occurring lactic acid bacteria could play a key role in promoting gut health and even combating harmful pathogens that cause foodborne illnesses.

Dr. Robert Kass | Beating arrhythmias with a heart in a dish
In the future, doctors will be able to create tiny replicas of your tissues in the lab, and then test them against a range of drugs, revealing exactly which treatments would work best for you before you even visit a drug store. This future of personalised medicine is driven by researchers such as Dr. Robert Kass of the Columbia University Medical Center. Kass and colleagues have pioneered the use of stem cells to develop personalized treatments for a genetic heart condition that disrupts normal heart rhythms. The researchers reprogrammed a patient’s skin cells into stem cells called induced pluripotent stem cells (or iPSCs for short), and they then induced the iPSCs to turn into heart cells. This allowed the research team to study how genetic mutations in the resulting heart cells affect the heart’s ion channels. Their research revealed that a mutation in a specific sodium channel was causing dangerous heart rhythms and that combining the drug mexiletine with a pacemaker device to increase heart rate, provided an effective and personalised treatment.
Dr James E. Goldman | Dr Osama Al-Dalahmah – Confronting the Challenge of Huntington Disease
Huntington disease (HD) is an inherited and progressive neurological disorder which is currently fatal. Dr James E. Goldman and Dr Osama Al-Dalahmah, both at Columbia University, USA, are utilising new techniques in molecular biology to better understand the brain pathology associated with HD. Their vision is to develop therapeutics that can slow the progression of the disease, and ultimately, treat and even prevent it.
Increase The Impact Of Your Research!
Explore partnership opportunities
Unwind without the hassle. Enjoy fresh audiobooks, delivered free!
