Finding Reefs: Advances in Mapping Rare Marine Habitats
Original Article Reference
This SciPod is a summary of the paper ‘Hydroacoustic Mapping of Geogenic Hard Substrates: Challenges and Review of German Approaches’ from Geosciences. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10030100
About this episode
The marine environment houses complex types of ecosystems that provide vital services and habitat to aquatic life. Areas of the seafloor where rocky outcrops are present, such as reefs and gravel beds, are some of the rarest marine habitats. Also known as ‘hard substrate habitats’ these ecosystems are under increasing pressure from fishing, eutrophication, climate change, and coastal management. Though hard substrates are protected in the European Union, we are unable to manage them effectively because maps describing their location and dimensions are inaccurate. In a review paper, Dr Svenja Papenmeier [Sven-yah Pah-pan-my-er] of Germany’s Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde summarises existing rules for mapping substrate habitats, and describes new and potentially ground-breaking mapping techniques.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. 
What does this mean?
Share: You can copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
Adapt: You can change, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
Credit: You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made.
More episodes
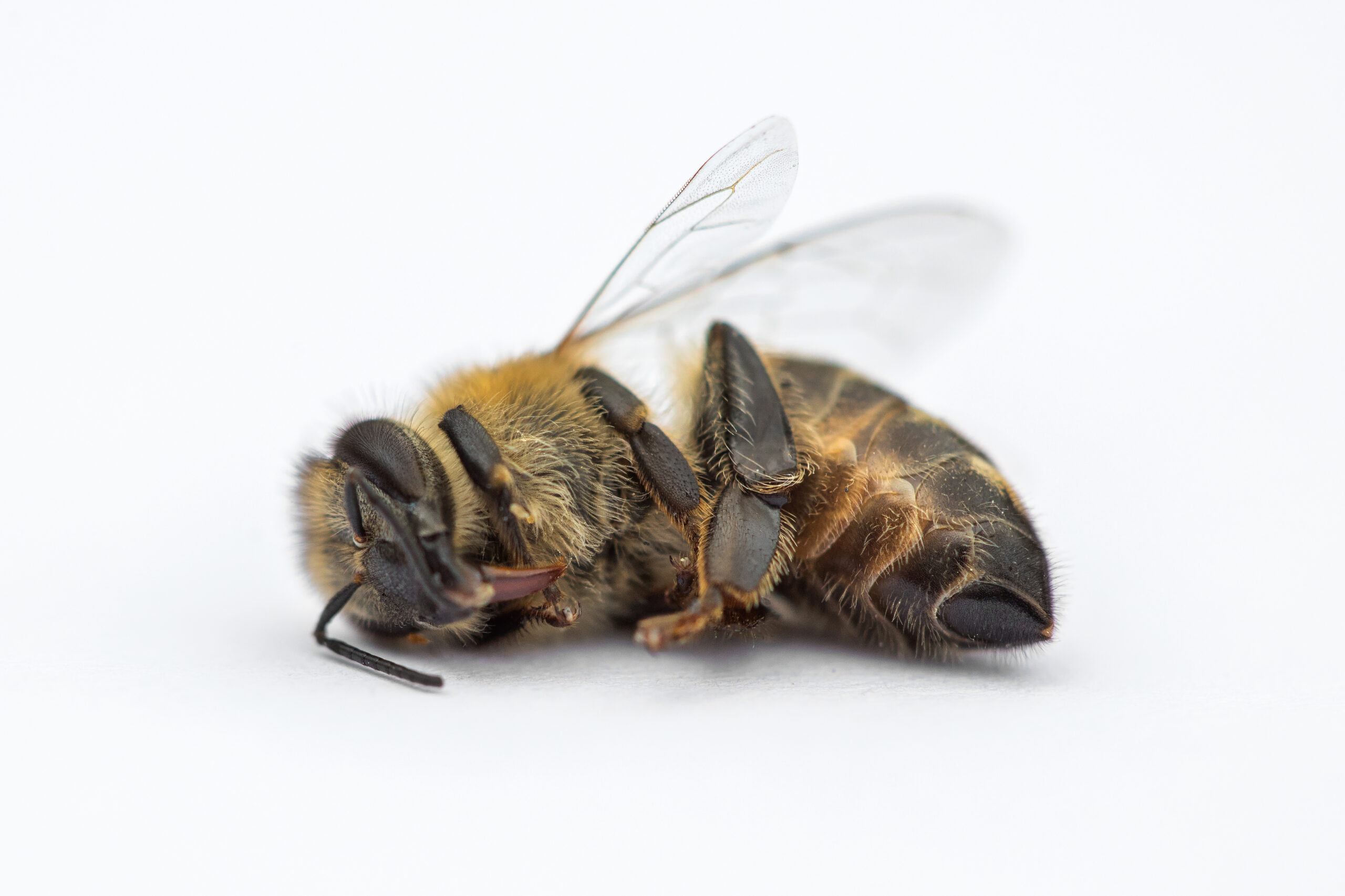
Pollinator Peril: How Common Agricultural Cocktails Harm Honeybees
Pollinators, including honey bees, wild bees, butterflies and many other insects, are some of the most important creatures on our planet. By pollinating plants, both wild and cultivated, they have an essential role in maintaining wider ecosystems and ensuring our food security. However, we have come to take them for granted, and don’t fully appreciate their function in ensuring our ongoing survival. Insects are declining at a truly alarming rate. Among other factors human activities such as industrial farming and corresponding insecticide and fungicide use over large areas of land to protect food crops against pests and disease are considered to be major contributors. Many different pesticides have also been detected in honeybee colonies. Scientists are attempting to uncover the specific factors involved in insect decline, before it’s too late. Recent research by Sarah Manzer and colleagues in the research groups of Prof. Ricarda Scheiner and Prof. Ingolf Steffan-Dewenter at the Julius Maximilians Universität Würzburg in Germany has shed new light on a potential culprit: a combination of insecticides and fungicides commonly used in agriculture.
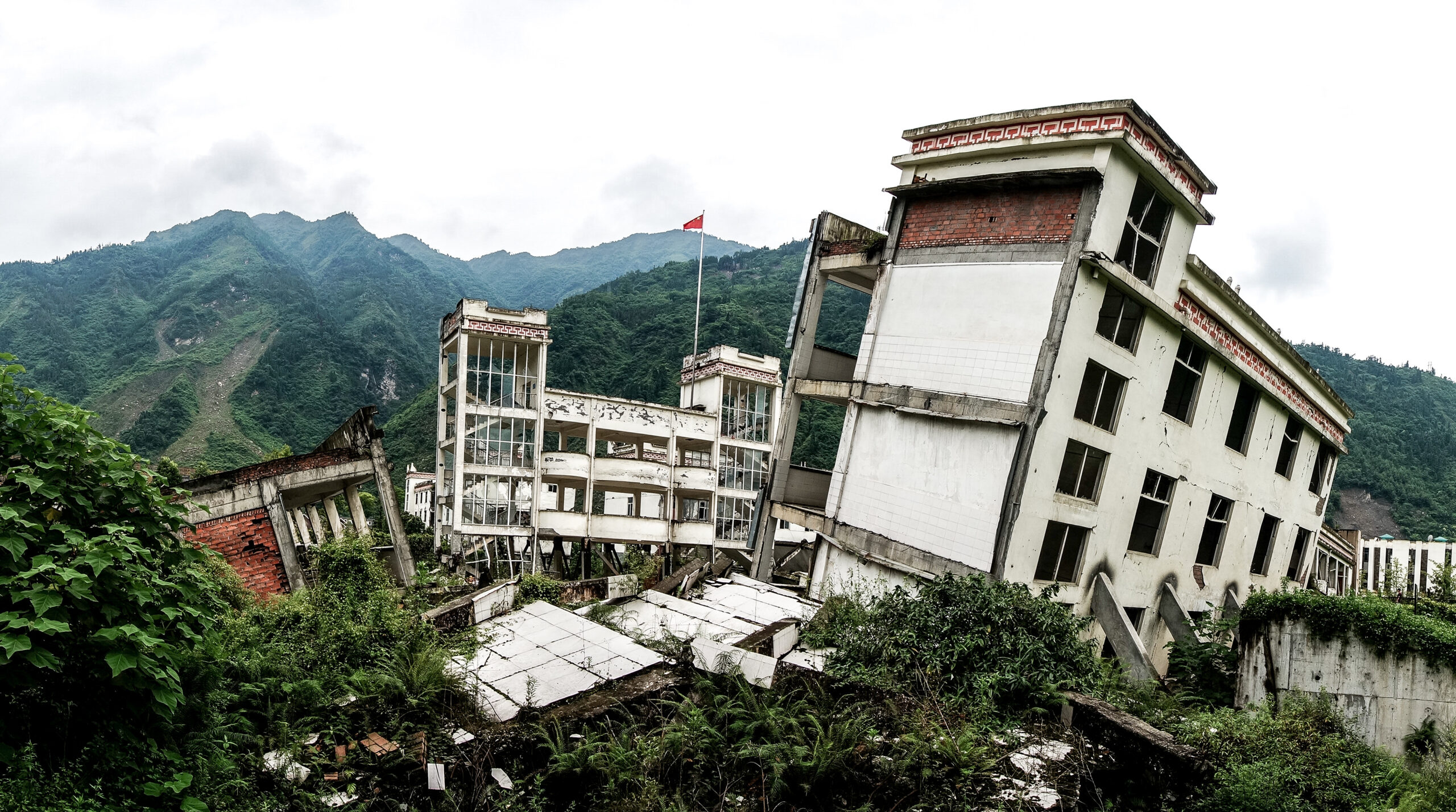
Dr. Zhe Su | Understanding the twisted tectonics of the Sichuan basin
The Sichuan basin in southern China is a region of deep geological and seismological complexity, which has so far prevented researchers from understanding its tectonic past. Through fresh analysis of previous observations, combined with the latest modelling techniques, a team led by Dr. Zhe Su at the National Institute of Natural Hazards, Beijing, suggests for the first time that the entire Sichuan basin is slowly rotating. Their result could explain the origins of one of the deadliest earthquakes in living memory, and could also help seismologists to better predict when earthquakes will strike the region in the future.
Dr. Claudia Ituarte-Lima – Dr. Radu Mares | How Latin America’s Groundbreaking Treaty Intersects with European Economic Law
Research by Dr. Claudia Ituarte-Lima and Dr. Radu Mares at Lund University examines how a pioneering environmental agreement in Latin America and the Caribbean introduces new ways of protecting nature and human rights. Their study reveals both opportunities and challenges in how this regional treaty interacts with European Union trade laws, offering insights into how different regions can work together to protect the environment and strengthen democracy.
Dr. Allen Place | Small but Deadly: The Tale of K. veneficum
The oceans, huge and brimming with diverse lifeforms, pose no less a struggle for survival for their inhabitants than that faced by creatures on dry land. Evolution has furnished marine organisms with huge array of defensive, and indeed, offensive adaptations to help them to thrive in this battleground. Among the organisms who live and compete in the ocean are dinoflagellates. These are small, single-celled creatures that are an important component of plankton found in marine ecosystems. Despite their tiny size, dinoflagellates such as Karlodinium veneficum can wield potent biochemical weaponry that gives them an edge against other competing organisms. Decades since the discovery of the toxic properties of Karlodinium veneficum, researchers such as Dr. Allen Place of the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Sciences, and his colleagues, have begun to unravel the secrets of its potent toxins, called karlotoxins. Their findings offer fascinating insights into the interactions of marine life and the weapons they adopt to capture prey and deter predators.
Increase the impact of your research
• Good science communication helps people make informed decisions and motivates them to take appropriate and affirmative action.
• Good science communication encourages everyday people to be scientifically literate so that they can analyse the integrity and legitimacy of information.
• Good science communication encourages people into STEM-related fields of study and employment.
• Good public science communication fosters a community around research that includes both members of the public, policymakers and scientists.
• In a recent survey, 75% of people suggested they would prefer to listen to an interesting story than read it.

Step 1 Upload your science paper
Step 2 SciPod script written
Step 3 Voice audio recorded
Step 4 SciPod published