Engineering and Technology
Explore Engineering and Technology

Dr Patrick O’Neill | Revolutionising Pharmaceutical Synthesis with Continuous Flow Chemistry
Dr Patrick O’Neill of Pfizer, Ireland, and Professor Jie Wu of the National University of Singapore, and their team, have made groundbreaking advancements in the synthesis of 1,2,3-triazole – a key building block in the manufacture of a life-saving antibiotic. Replacing traditional batch processes, they developed a safer, more efficient method using continuous flow chemistry, which addresses potential global supply chain vulnerabilities. This innovative approach eliminates hazardous intermediates, improves reaction safety, and ensures a stable supply of 1,2,3-triazole for global pharmaceutical production.
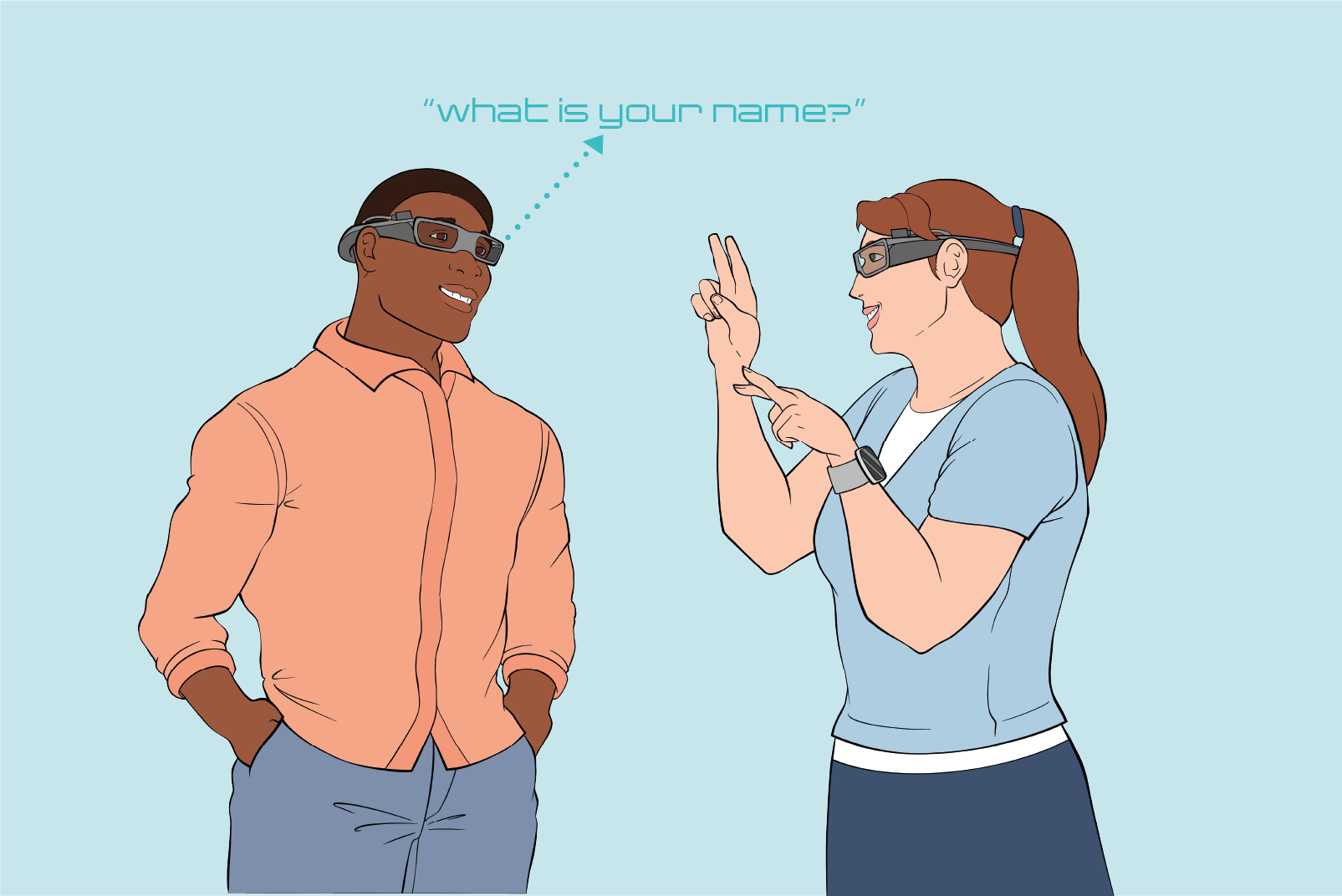
Dr Ramtin Zand | A Hybrid System for Real-Time Sign Language Translation
Neuromorphic computing is a powerful tool for identifying time-varying patterns, but is often less effective than some AI-based techniques for more complex tasks. Researchers at the iCAS Lab directed by Ramtin Zand at the University of South Carolina, work on an NSF CAREER project to show how the capabilities of neuromorphic systems could be improved by blending them with specialized machine learning systems, without sacrificing their impressive energy efficiency. Using their approach, the team aims to show how the gestures of American Sign Language could be instantly translated into written and spoken language.
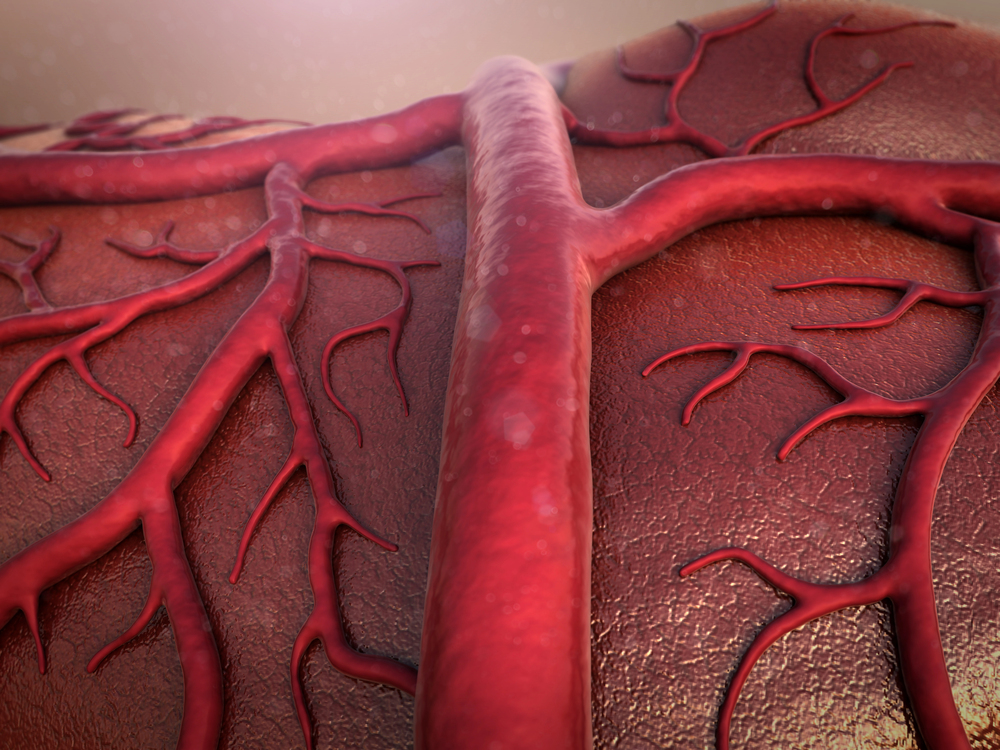
Dr. Mingjun Xie | A Blueprint for Life: Creating Blood Vessels in Bioprinted Tissues
A future where injured or diseased organs can be removed and replaced with new lab-printed tissues that are customized specifically for each patient is not as far away as you might think. These functional and living tissues could grow naturally within the body, and repair and sustain themselves over time. While these concepts were once in the realm of science fiction, advances in bioprinting, which is a form of 3D printing using biological “inks” (known as bioinks) loaded with living cells, are bringing them closer to reality. Among the researchers advancing this field is Dr. Mingjun Xie of Zhejiang University, China, and colleagues, who are performing work that addresses a significant challenge in bioprinting. This involves creating large portions of tissues that have a functional vasculature, thereby mimicking the complexity of native tissues and organs.

Professor Christophe Ley | Spotting relationships in complex angular datasets
Data involving angles can be found across a diverse array of scientific fields, but so far, the mathematical tools used to study them have often proved insufficient to detect the complex relationships between different angles within large datasets. Through its research, a team consisting of Professor Christophe Ley and Sophia Loizidou from the University of Luxembourg, Professor Shogo Kato from the Institute of Statistical Mathematics in Tokyo, and Professor Kanti Mardia from the University of Leeds, has developed a new model which overcomes many of these challenges: allowing the researchers to study relationships between three angles at once, as well as mixtures of angles and classical measurements on the line.

Dr. Chance Glenn | Could extreme electric fields make the warp drive a reality?
For decades, works of science fiction have explored how the universe’s most fundamental speed limit could be broken by warping the fabric of spacetime. Through his experiments, Dr. Chance Glenn, founder of Morningbird Space Corporation, believes he may have discovered how spacetime can be distorted by extreme electric fields, which can be easily created in the lab. If his theory is correct, it would mean that the concept of ‘warp drives’ which allow us to travel at faster than the speed of light could be more feasible than we once thought.
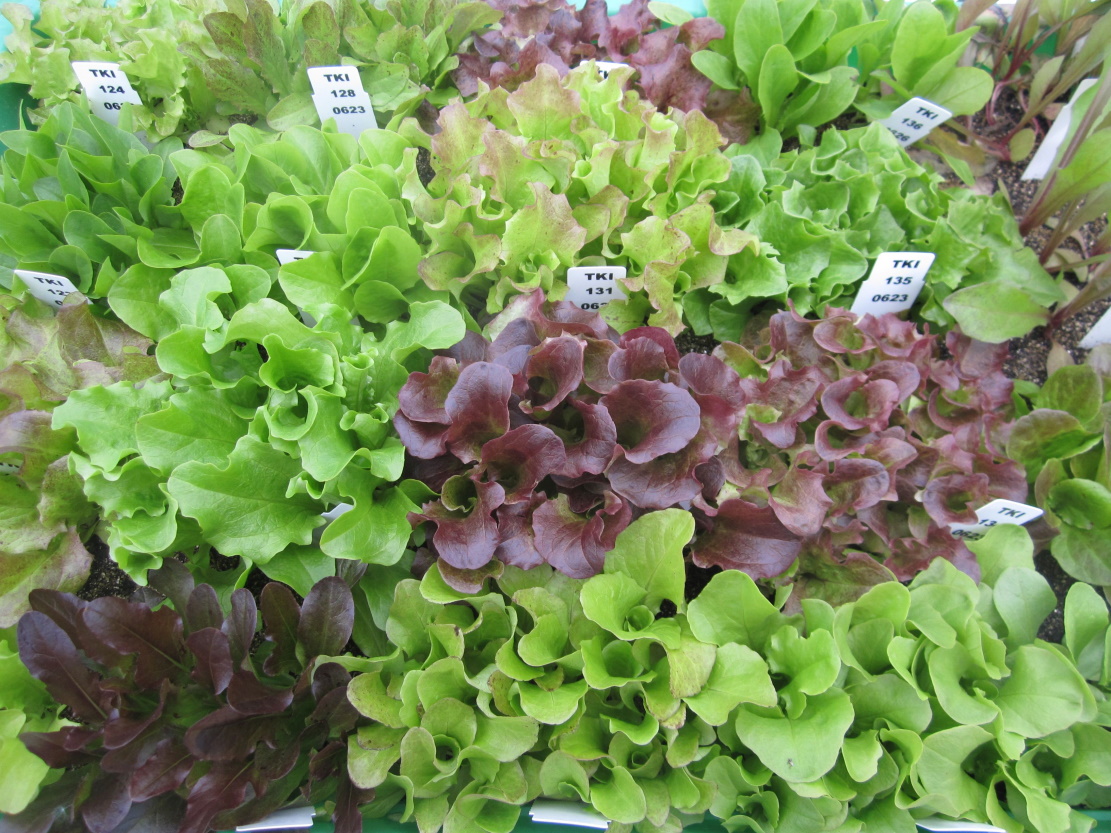

Dr Sandra Goritschnig – Dr Pasquale Tripodi | The Science of Greens: Using Genetic Insights to Cultivate Better, Stronger Lettuce
In recent years, rapid advancements in techniques for genetic analysis and manipulation have enhanced our potential to understand and improve crop diversity. An innovative project led by Dr. Pasquale Tripodi of the Italian Council for Agricultural Research and Economics and Dr Sandra Goritschnig of the European Cooperative Programme for Plant Genetic Resources marks a significant advance in the study of lettuce genetics. Their recently published research platforms a highly sophisticated technique to analyse genetic diversity within lettuces called Single Primer Enrichment Technology, or SPET for short. This approach provides a highly detailed view of lettuce genetics and also has significant implications for agricultural resilience and crop selection and breeding.

Dr. Robert Tomkowski | Investigating How Dimpled Surfaces Can Minimise Friction
Dimpled surfaces offer a useful and easily implementable way to reduce friction between lubricated surfaces as they slide over each other. Through cutting-edge simulations, Dr. Robert Tomkowski and colleagues at the KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Sweden explore how the microscale structures of surface dimples can be optimized to minimize friction. Their findings could help to reduce wear in mechanical systems, while also making them more energy efficient.
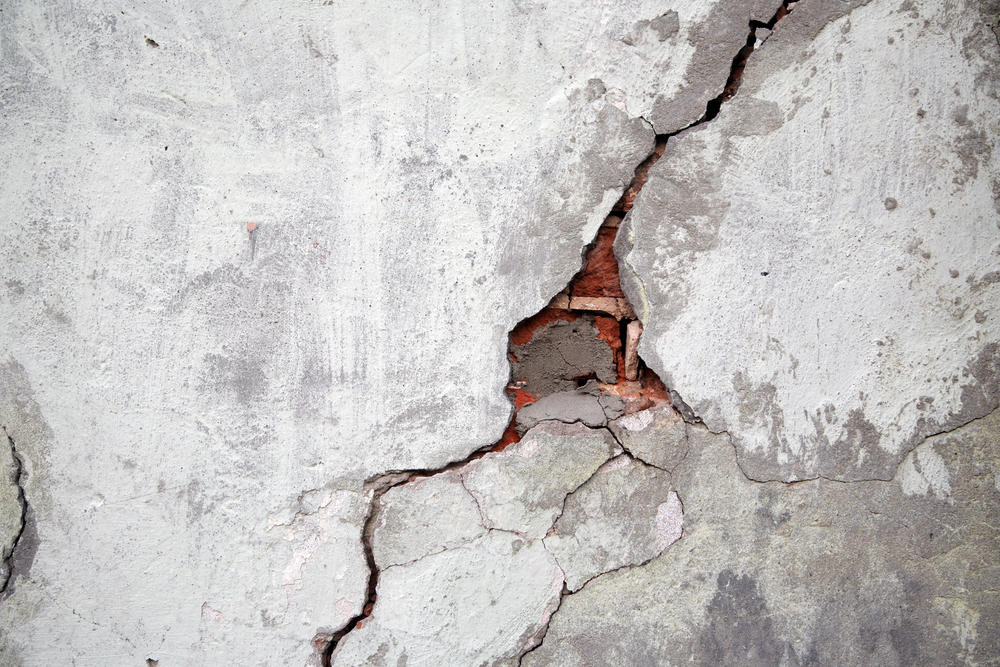

Professor Suzanne Scarlata – Dr. Nima Rahbar | How a Biological Enzyme Could Help Concrete to Heal Itself
As an inherently brittle material, concrete often needs to be replaced after just a few decades: driving a demand which incurs significant costs for Earth’s climate. Through their research, Professors Suzanne Scarlata and Nima Rahbar at Worcester Polytechnic Institute, Massachusetts, introduce a new mechanism that allows concrete to quickly repair itself, with the help of an enzyme vital to the function of living cells. This approach could help to reduce the world’s insatiable demand for concrete.
Lixiang Zhang | Seeing the Full Picture: The CPS-Merge Approach to Assess Complex Datasets
In the age of big data, and particularly in specialisations such as artificial intelligence, biology, and medicine, researchers often generate large and complex datasets that are challenging to analyse. This is particularly true for multi-view data, otherwise known as multimodal data, which are data that encompass multiple perspectives concerning a single entity or phenomenon. In the case of single-cell genomics, for instance, researchers can measure a huge range of different characteristics concerning an individual cell, such as RNA expression levels or protein levels. While multi-view datasets provide vast amounts of information, they are difficult to analyse because looking at each type of data within them provides only a small part of the overall picture. A new computational approach called Covering Point Set-merge analysis, or CPS-merge analysis for short, has been developed by Lixiang Zhang of Pennsylvania State University and colleagues, and it aims to assist researchers to merge the different types of data present in multi-view datasets into one coherent and meaningful set of results, without misrepresenting the individual contributions of each type of data.
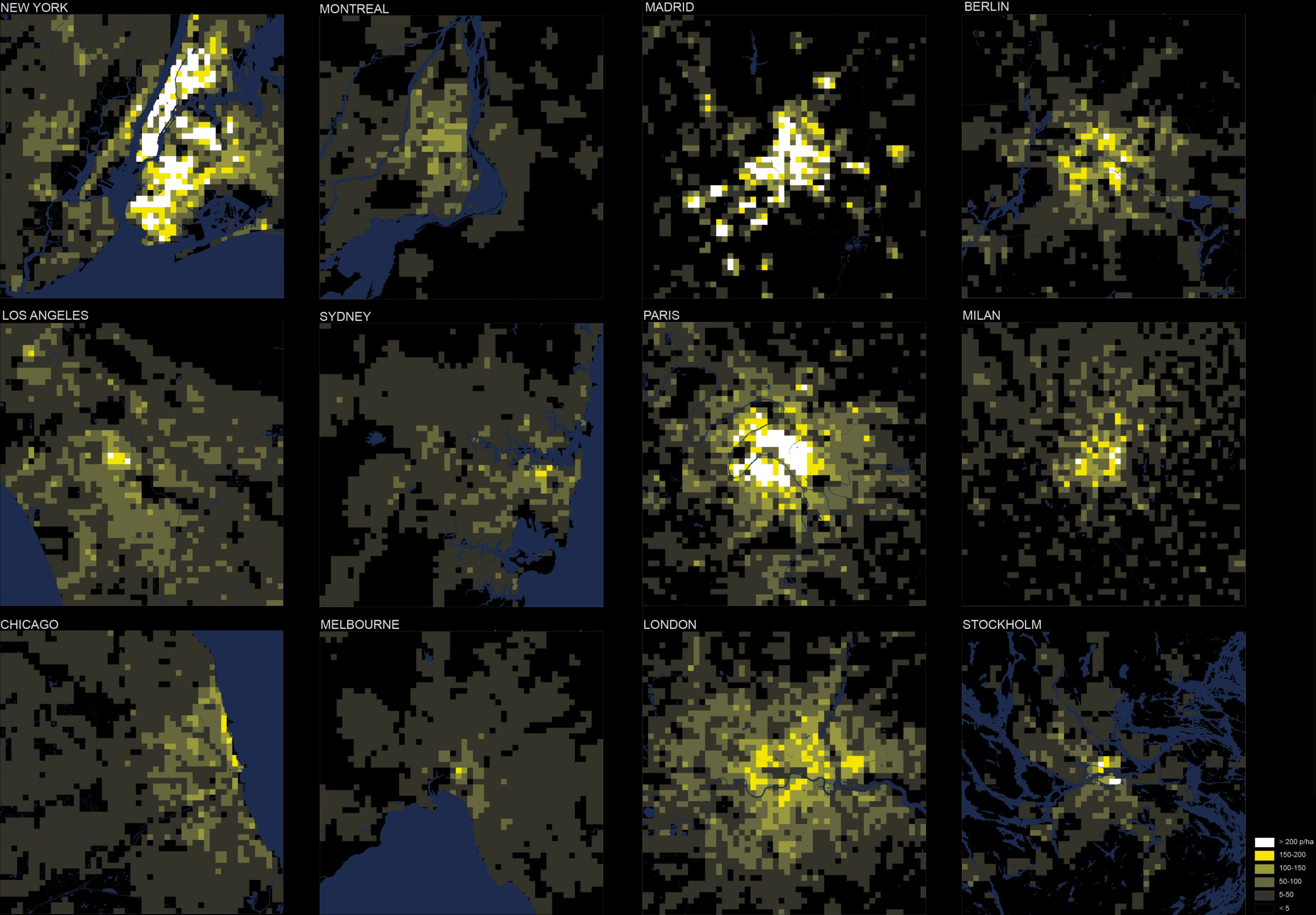
Dr Elek Pafka | Mapping urban density from the neighbourhood to the metropolis
So far, approaches to mapping the density of cities have often been oversimplified, causing them to overlook many key aspects of everyday urban life. Through his research, Dr Elek Pafka at the University of Melbourne introduces two new metrics for measuring urban density, which better capture its complex, multi-scale variations. His research offers deeper insights into how people experience and interact with cities, and could lead to new strategies to make our cities more productive, sustainable, and better places to live.
Dr Di Yun | Lessons from Tai-Chi could make Travelling Wave Reactors a reality
In principle, travelling wave reactors offer a safe, highly efficient approach to generating nuclear power. However, development has been held back by a variety of challenges linked to the need for extensively high burn-up in the reactor core, meaning very high rates of generated energy which can damage the reactor. Inspired by the principles of Tai-Chi, a team led by Di Yun from Xi’an Jiaotong University has shown that with the right approach, a high temperature operation, usually deemed as a threat, can be transformed into useful advantages, bringing the practical rollout of travelling wave reactors one step closer to reality.
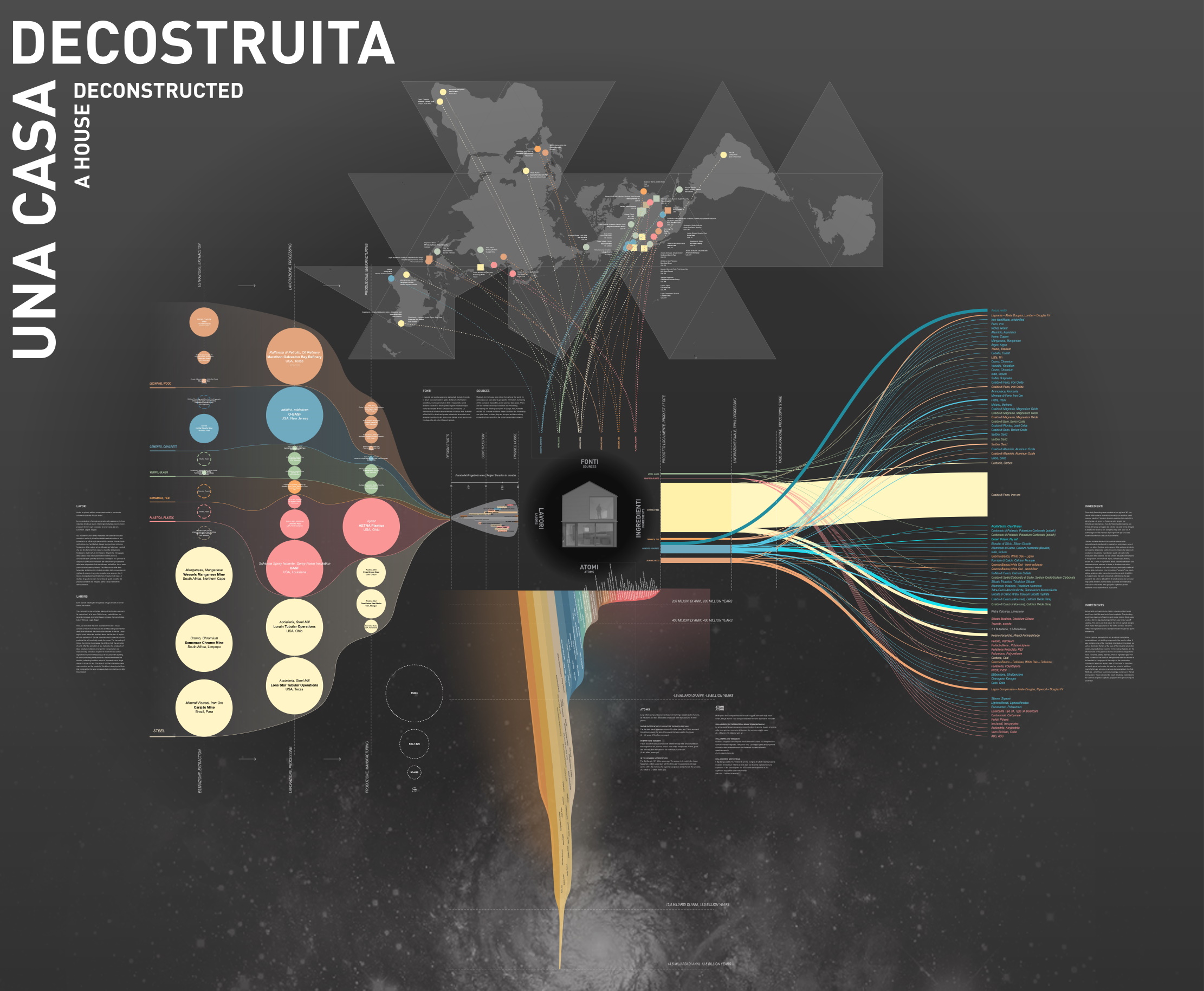
Professor Mark Jarzombek | A House Deconstructed: Uncovering the Hidden History of the Modern House
The full extent of the labour and resources which go into creating a modern house is hidden deeply within the buildings we call home. Professor Mark Jarzombek of MIT and Professor Vikramaditya Prakash of the University of Washington are co-founders of the Office of Uncertainty Research, a research collaboration that is dedicated to rethinking architecture in a modern context. Through their research, Jarzombek and Prakash investigate these hidden stories by exploring the history of a recently built modern house in Seattle. Their findings reveal that the presumed transparency of modern architecture conceals deep ethical and environmental challenges, inspiring a call for a critical reassessment of how our current construction practices should be understood and approached.
Increase The Impact Of Your Research!
Explore partnership opportunities
Stay Up To Date With SciPod
Subscribe to receive our latest SciPods straight to your mailbox
