
by admin | Jul 27, 2022 | biology, earth and environment
Cowpea is an extremely versatile food crop. Packed with high-quality protein, it has become a staple legume in many households in Africa, where it is indigenous. Cowpea also cycles nutrients back into the soil, supporting sustainable farming and healthy ecological networks. However, the production of this sustainable crop faces many hurdles, including drought, pesticide use, and declining soil quality. In a recent review, Professor Olubukola Oluranti Babalola of North-West University in South Africa outlines the issues facing cowpea production and highlights potential solutions.

by admin | Jul 6, 2022 | earth and environment, physical sciences
Gyroscopes are widely used to measure the orientations and rotation speeds of moving objects – but according to one pair of researchers, the techniques we currently use to measure them are introducing significant and easily avoidable errors. Through their research, Dr Sara Stančin | Dr Sašo Tomažič, both at the University of Ljubljana in Slovenia, introduce a mathematical framework which accounts for how all three rotations measured by a gyroscope happen simultaneously, rather than in a sequence.
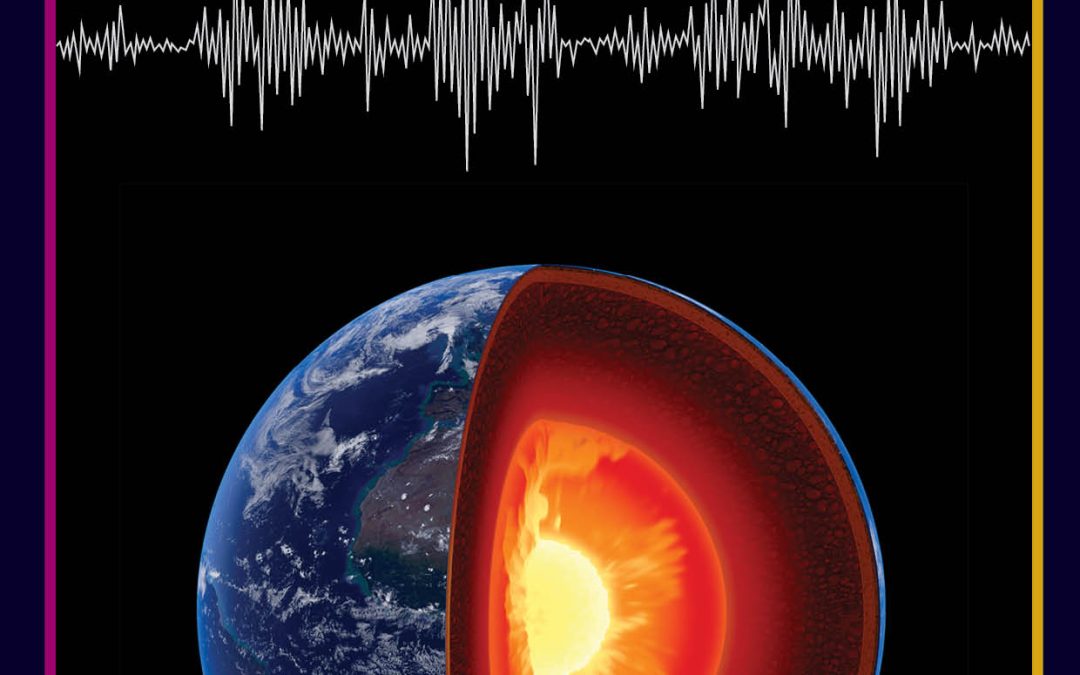
by admin | Jul 6, 2022 | earth and environment, engineering and tech
The magnetic field that enshrouds Earth is generated by processes deep within the planet’s interior, which geologists still don’t fully understand. Among the effects that remain poorly studied are brief variations in the strength of the magnetic field, which occur over timescales of several decades. Through detailed mathematical analysis, Dr Klaudio Peqini and Professor Bejo Duka, both at the University of Tirana in Albania, explore how these variations could arise from changes in the flows of material at the boundary between Earth’s core, and its thick layer of mantle.
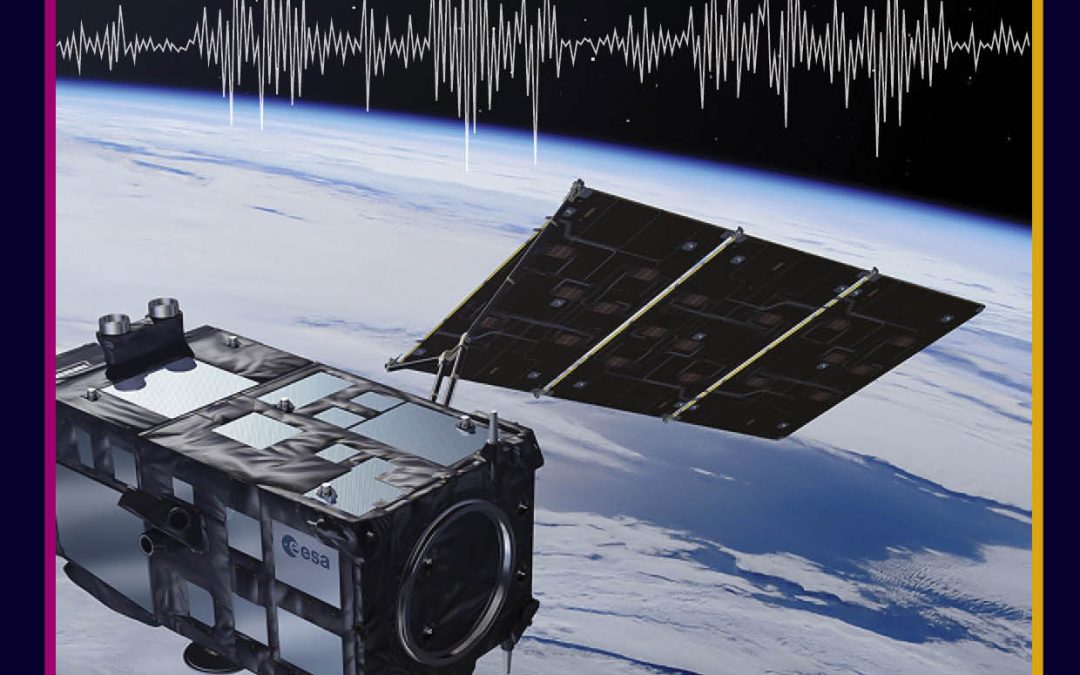

by admin | Jul 6, 2022 | earth and environment, engineering and tech
Across the globe, climate change is driving extreme weather events, such as floods and droughts, with increasing frequency, duration, and intensity. Accurately assessing the flow of water through rivers – or river discharge – could help us forecast extreme weather events and prevent loss of life. Sensors onboard satellites could provide more accurate and in-depth measurements of river variables than ever before. As part of the RIDESAT project, funded by the European Space Agency, Dr Angelica Tarpanelli and her team of researchers from Italy and Denmark investigate how combining remote sensing data from satellites could support river discharge assessments.
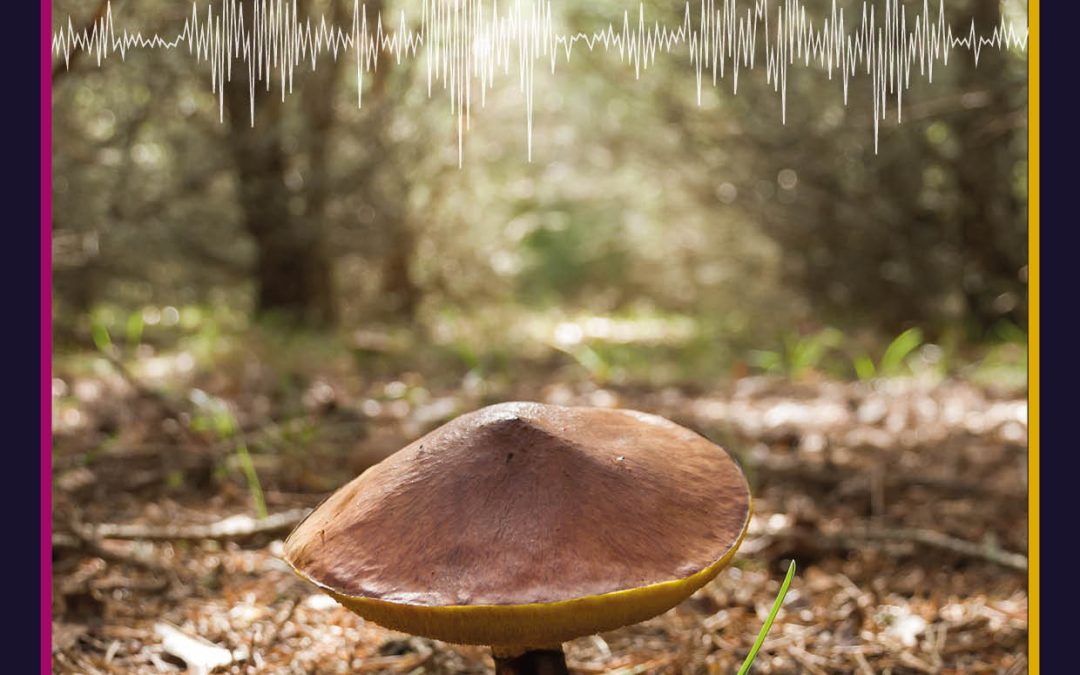

by admin | Jun 9, 2022 | biology, earth and environment, trending
An ancient relationship between plants and fungi could help us improve forestry and agriculture, while also responding to the challenges posed by climate change. These beneficial fungi, along with their bacteria helpers, help plants to grow bigger and healthier, and survive droughts. An international team of researchers has been investigating how these fungi and bacteria increase mineral availability for Scots pine and red pine seedlings through mineral weathering.
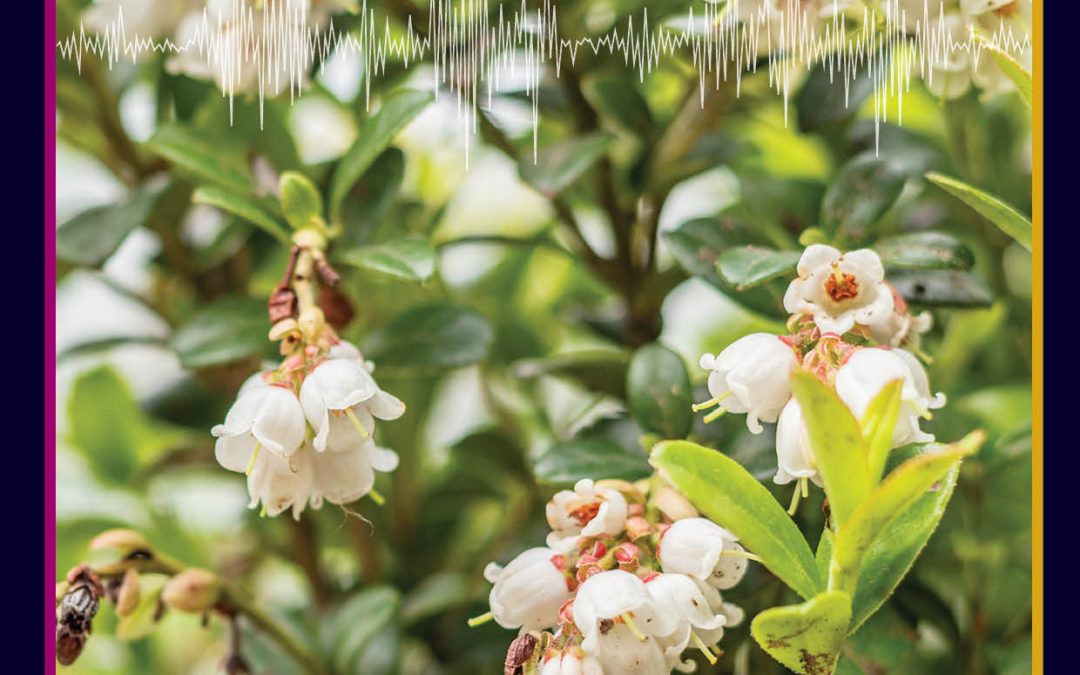

by admin | May 18, 2022 | biology, earth and environment, earth and environment animated, research animated
A welcome sign of a change in seasons, the year’s first flowers usher in the start of spring. Yet, as the climate warms, some flowers are blooming earlier. Since plants respond to environmental cues, such as temperature, shifts in their annual development has long been considered an effect of climate change. However, significant warming does not always lead to earlier flowering.
Page 7 of 28« First«...56789...20...»Last »






