Earth and Environment
Explore Earth and Environment

Pollinator Peril: How Common Agricultural Cocktails Harm Honeybees
Pollinators, including honey bees, wild bees, butterflies and many other insects, are some of the most important creatures on our planet. By pollinating plants, both wild and cultivated, they have an essential role in maintaining wider ecosystems and ensuring our food security. However, we have come to take them for granted, and don’t fully appreciate their function in ensuring our ongoing survival. Insects are declining at a truly alarming rate. Among other factors human activities such as industrial farming and corresponding insecticide and fungicide use over large areas of land to protect food crops against pests and disease are considered to be major contributors. Many different pesticides have also been detected in honeybee colonies. Scientists are attempting to uncover the specific factors involved in insect decline, before it’s too late. Recent research by Sarah Manzer and colleagues in the research groups of Prof. Ricarda Scheiner and Prof. Ingolf Steffan-Dewenter at the Julius Maximilians Universität Würzburg in Germany has shed new light on a potential culprit: a combination of insecticides and fungicides commonly used in agriculture.
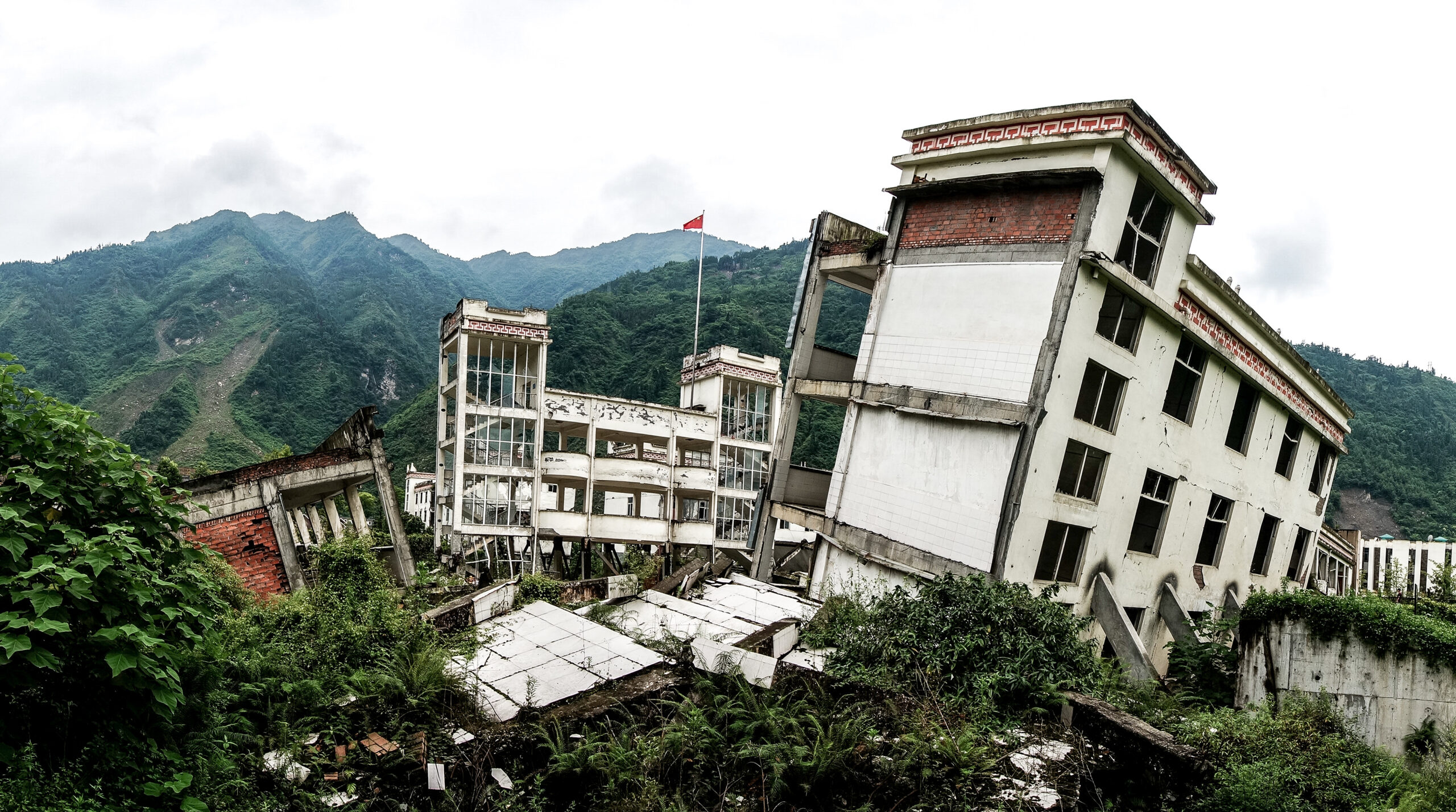

Dr. Zhe Su | Understanding the twisted tectonics of the Sichuan basin
The Sichuan basin in southern China is a region of deep geological and seismological complexity, which has so far prevented researchers from understanding its tectonic past. Through fresh analysis of previous observations, combined with the latest modelling techniques, a team led by Dr. Zhe Su at the National Institute of Natural Hazards, Beijing, suggests for the first time that the entire Sichuan basin is slowly rotating. Their result could explain the origins of one of the deadliest earthquakes in living memory, and could also help seismologists to better predict when earthquakes will strike the region in the future.

Dr. Claudia Ituarte-Lima – Dr. Radu Mares | How Latin America’s Groundbreaking Treaty Intersects with European Economic Law
Research by Dr. Claudia Ituarte-Lima and Dr. Radu Mares at Lund University examines how a pioneering environmental agreement in Latin America and the Caribbean introduces new ways of protecting nature and human rights. Their study reveals both opportunities and challenges in how this regional treaty interacts with European Union trade laws, offering insights into how different regions can work together to protect the environment and strengthen democracy.
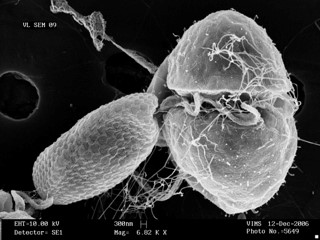
Dr. Allen Place | Small but Deadly: The Tale of K. veneficum
The oceans, huge and brimming with diverse lifeforms, pose no less a struggle for survival for their inhabitants than that faced by creatures on dry land. Evolution has furnished marine organisms with huge array of defensive, and indeed, offensive adaptations to help them to thrive in this battleground. Among the organisms who live and compete in the ocean are dinoflagellates. These are small, single-celled creatures that are an important component of plankton found in marine ecosystems. Despite their tiny size, dinoflagellates such as Karlodinium veneficum can wield potent biochemical weaponry that gives them an edge against other competing organisms. Decades since the discovery of the toxic properties of Karlodinium veneficum, researchers such as Dr. Allen Place of the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Sciences, and his colleagues, have begun to unravel the secrets of its potent toxins, called karlotoxins. Their findings offer fascinating insights into the interactions of marine life and the weapons they adopt to capture prey and deter predators.

Dr. Andrea Grindeland | The Tiny Heroes That Could Save Deer and Elk from Chronic Wasting Disease
It’s not difficult to picture a lush forest landscape populated with majestic deer and elk, long admired for their prowess and strength. Now, imagine that same scene, but instead of healthy and happy animals browsing a forest ecosystem, we see creatures that are thin and disoriented, that struggle to run or even stand, with halting and confused movements that are pitiable and distressing to watch. This is the harsh reality of Chronic Wasting Disease, an illness that currently has no cure and that threatens such wildlife around the world. Part of the challenge with Chronic Wasting Disease is the difficulty in studying it reliably in wildlife. The disease has subtle signs at an early stage, and it is difficult to obtain robust and reproducible data from large, wild animals who often live in remote and poorly accessible forest ecosystems. Consequently, researchers have turned to an unlikely but powerful ally, the tiny laboratory mouse, to model and study the disease under laboratory conditions. Dr. Andrea Grindeland of the McLaughlin Research Institute, and her colleagues, have authored a review of the existing mouse models of Chronic Wasting Disease. These tiny creatures have been engineered to mimic the biology of cervids, such as deer and elk, and are providing crucial insights into how Chronic Wasting Disease evolves, is transmitted, and how it might one day be controlled or even eradicated.

Dr Yvette Gramlich | How bursts of biomass burning can impact the Arctic
The Arctic’s climate is changing faster than almost anywhere else on Earth, but climate scientists are still uncertain how it is being affected by carbon-rich aerosols, released by fires thousands of kilometres to the south. Through their research, a team led by Dr Yvette Gramlich at Stockholm University in Sweden and the Paul Scherrer Institute in Switzerland has gained deeper insights into how these aerosols are impacting Earth’s northernmost reaches. Their work could help climate scientists to better predict how the Arctic’s climate will change in the future.
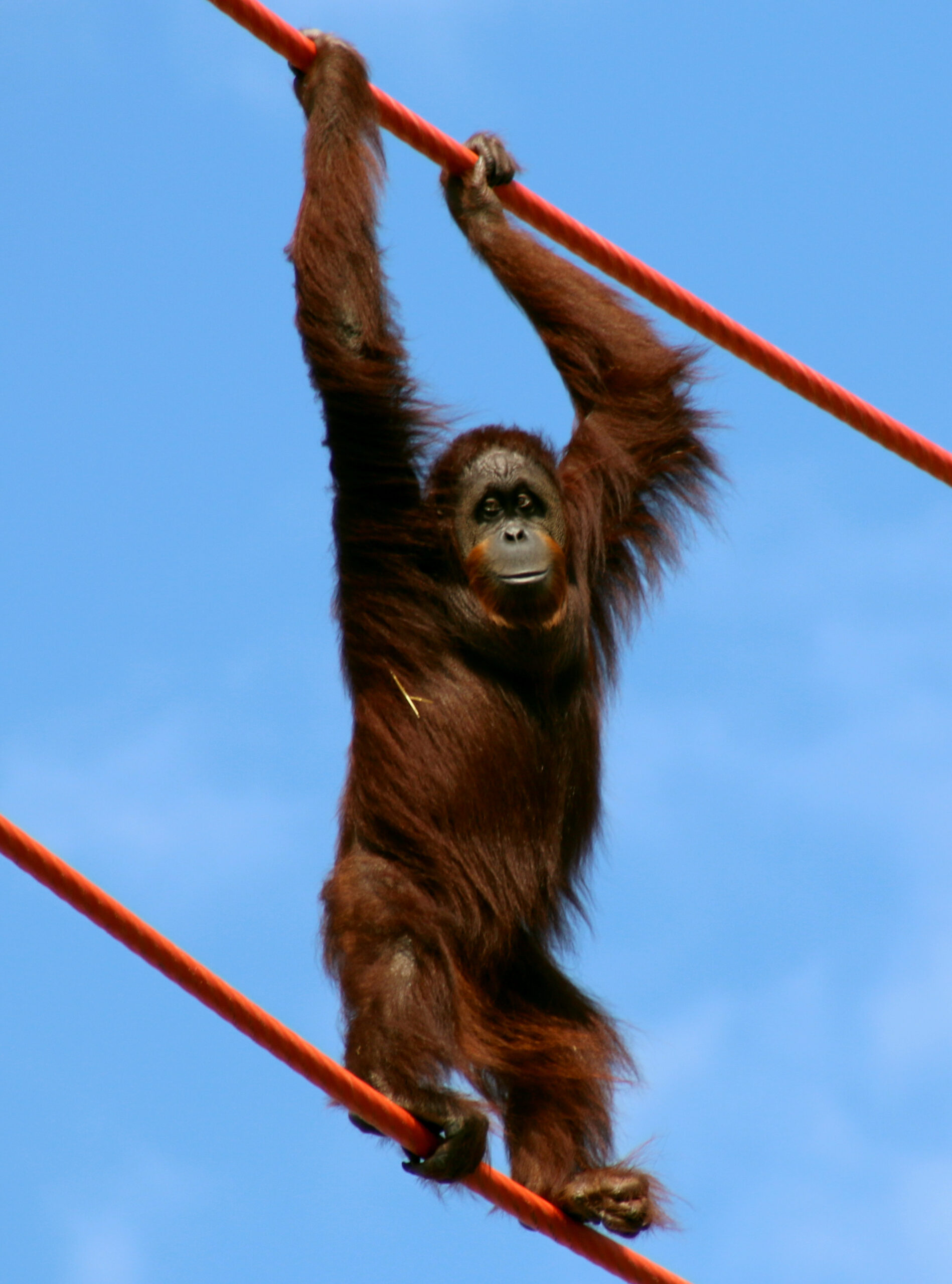

Dr Robert Shumaker | What Orangutan Tool Use Tells Us About Human Evolution
Humans aren’t the only species that use tools, many animals do. Our closest relatives, the great apes, have long been known for their intelligence and ability to manipulate objects in their environment. Among the great apes, orangutans stand out for their complex tool use, which may hold important clues about how early human technologies evolved. A recent Outlook article authored by Dr. Robert Shumaker and Dr. Christopher Martin, both of the Indianapolis Zoo, delves into the existing research into ways that orangutans use stone tools, exploring the cognitive processes behind this behavior and what it can tell us about human evolution.

Dr. Kurt Vollmer | Weeding Out the Competition: The Promise of Cover Crops in Sustainable Agriculture
As global agriculture faces increasing challenges from climate change, soil degradation, and herbicide resistance, sustainable practices are becoming more crucial than ever. Among these practices, the use of cover crops, a technique that has been gaining traction for its multiple benefits, stands out. Dr. Kurt Vollmer and his colleagues at the University of Maryland and Rutgers University have delved into this area, focusing on the potential of spring-seeded grass cover crops in improving weed management and crop yields, specifically in cucurbit production. Their research sheds light on how integrating cover crops with traditional farming techniques can lead to more sustainable and productive agricultural systems.

Dr Luis Gimeno-Sotelo | Statistical evidence of the link between drought and atmospheric moisture transport
Much of the world’s rainfall is triggered by the transport of moisture along corridors high up in the atmosphere. Through fresh analysis of historical climate data, Luis Gimeno-Sotelo and colleagues at the University of Vigo have shown for the first time how the causes of certain droughts can be directly linked with a lack of moisture being transported along these corridors. Their results could help climate scientists to better predict when and where droughts will occur in the future.
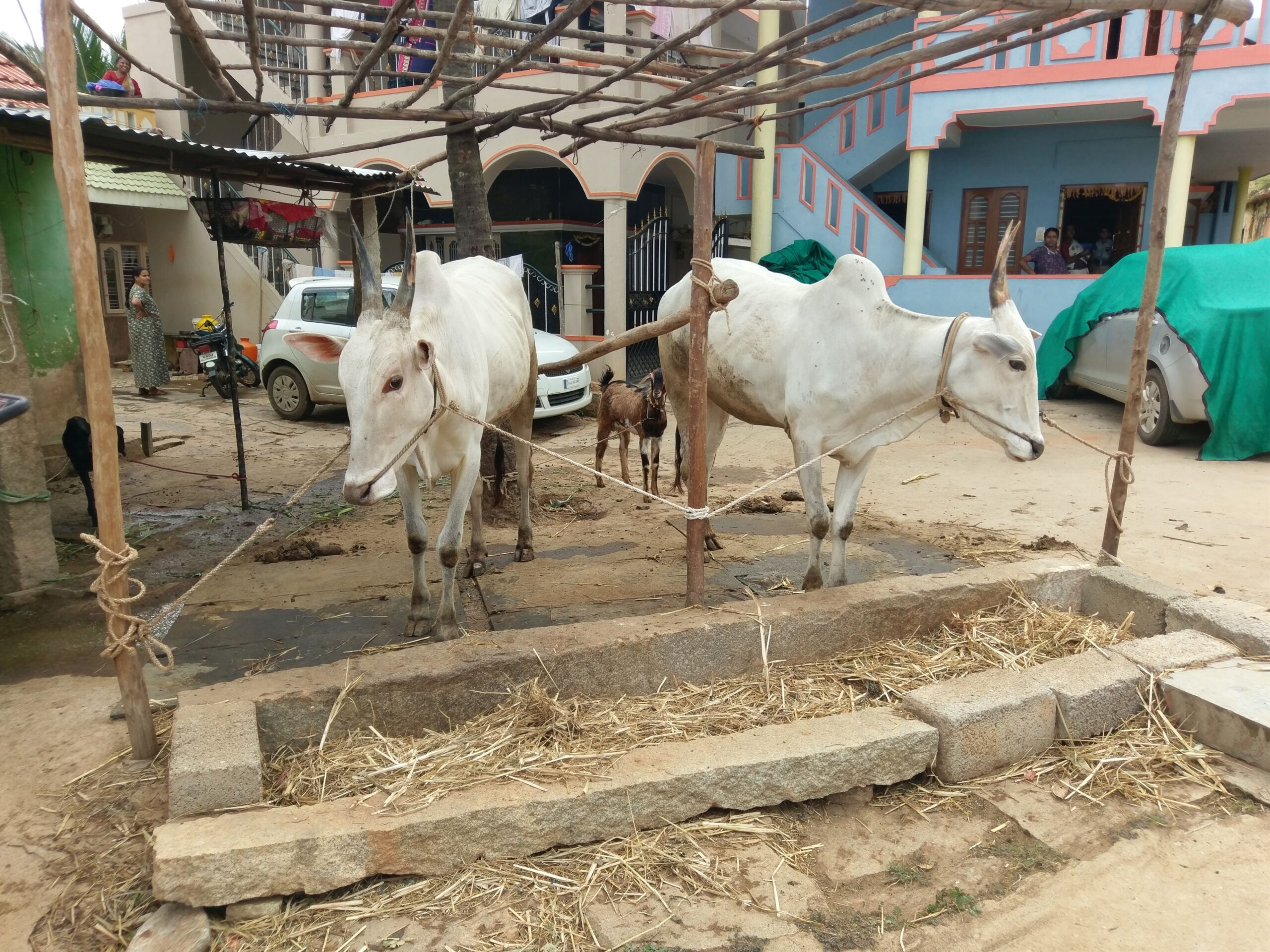

Dr. Ellen Hoffmann | Rurbanity: How rural and urban phenomena intermingle worldwide
Over the next few decades, the Earth’s urban population is set to explode, with the large majority of growth happening in cities across the Global South. A team of researchers at the Universities of Kassel and Göttingen, led by Prof. Andreas Bürkert and Prof. Nikolaus Schareika, predicts that these changes will be widely characterized by a merging of rural and urban features: a concept defined as ‘rurbanity’ in a recent landmark publication authored by Dr. Ellen Hoffmann and colleagues. By studying this phenomenon closely, the team aims to support cities in the Global South in their efforts to better prepare for the challenges to come. The concept is comprehensive enough to allow researchers to also understand ongoing processes of change in more mature cities of the North, such as climate-smart and socially inclusive adaptations, through the lens of rurbanity.

Prof. Mark Kimsey | The Earth’s Blueprint: How Soil Origins Guide Forest Management
Forests are more than just a collection of trees; they are dynamic ecosystems that depend on a variety of factors to thrive. One of the most crucial yet often overlooked components of these ecosystems is the soil. Far from being just a passive foundation, soil is an active, living system that plays a vital role in determining the health and productivity of forests. A recent study by emeritus Professor James Moore of the University of Idaho and his colleagues offers a deep dive into how the geological origins of soil influence its chemical properties, shedding light on the intricate relationships between soil, vegetation, and forest management in the Inland Northwest region of the United States.
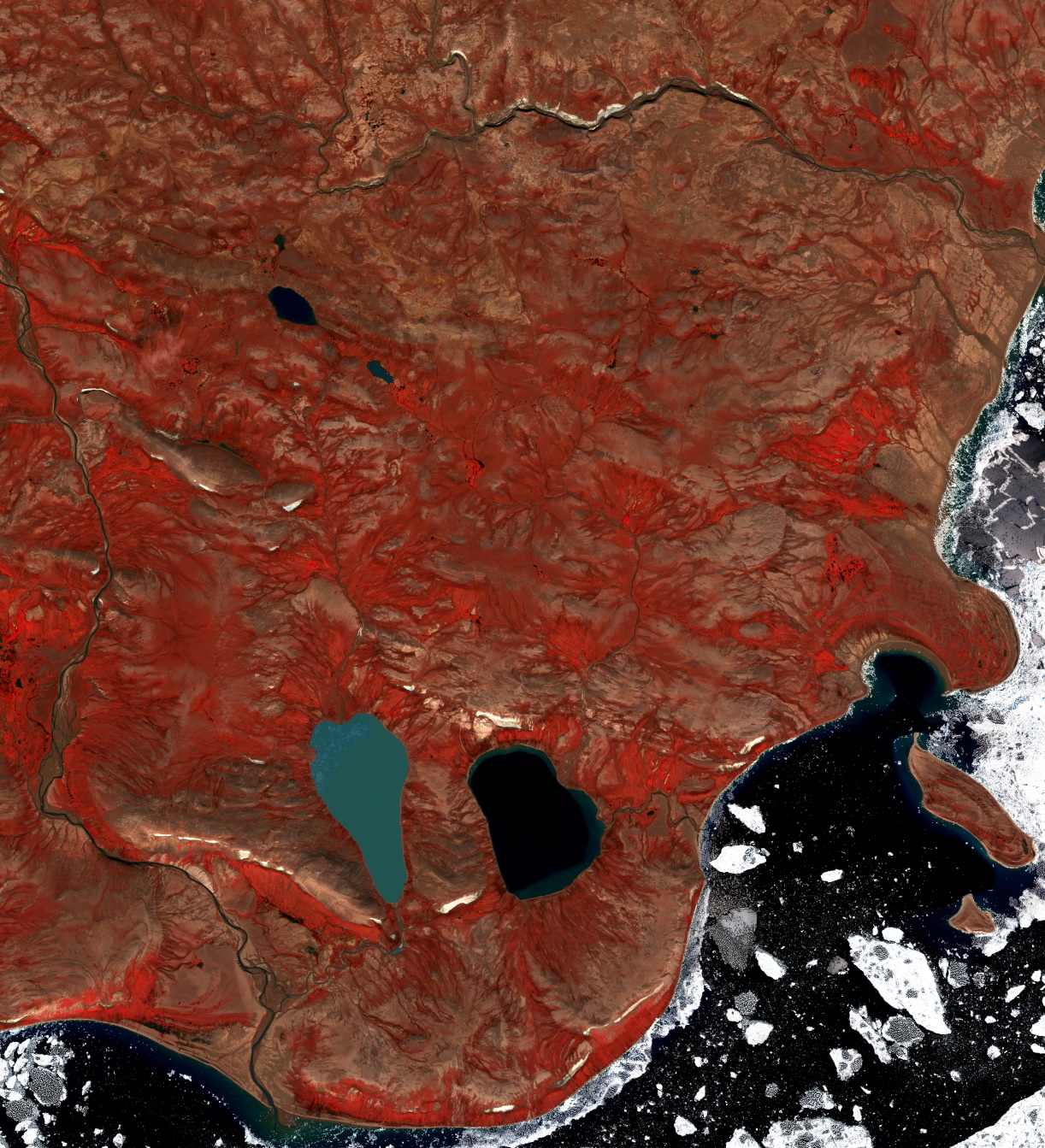
Professor Paul Treitz | Mapping Environmental Change: Remote Sensing at the Frontlines of the Canadian Arctic
The Arctic is warming at a rate of three to four times faster than the global average; a phenomenon known as Arctic amplification. This is, in large part, a result of warming atmospheric temperatures causing a decline in snow and ice cover at high latitudes. This, in turn, increases the amount of solar energy absorbed by marine and terrestrial surfaces. As a result, near surface temperatures continue to increase, resulting in a further reduction of snow and ice. This represents a positive feedback where increased temperatures are coupled with a decline in snow and ice cover.
Increase The Impact Of Your Research!
Explore partnership opportunities
Unwind without the hassle. Enjoy fresh audiobooks, delivered free!
