A Personalised Mathematical Model for Anaemia in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease – Dr Doris H. Fuertinger, Fresenius Medical Care
Original Article Reference
This SciPod is a summary of the paper ‘Prediction of haemoglobin levels in individual hemodialysis patients by means of a mathematical model of erythropoesis’, from the open access journal PLOS ONE: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0195918
Share Episode
About this episode
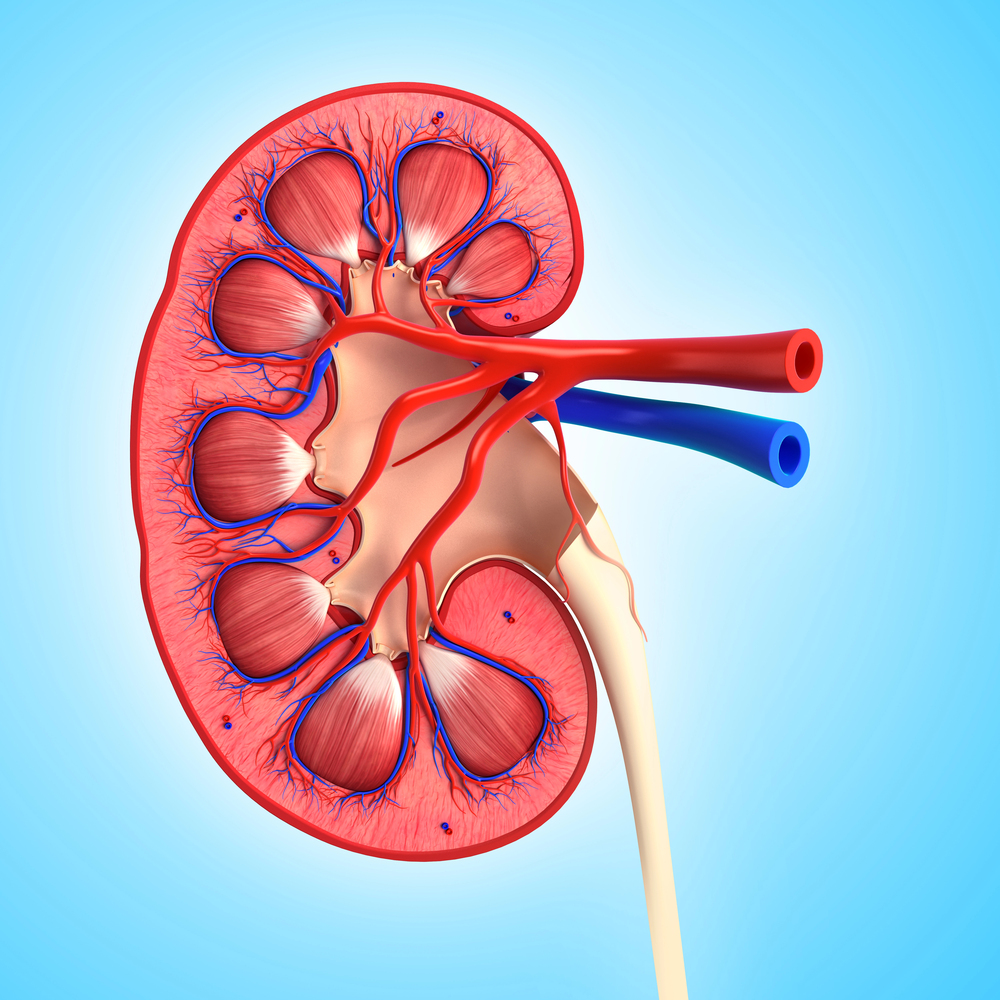
Individuals with chronic kidney disease commonly also suffer from renal anaemia. Renal anaemia, a condition in which individuals lack enough red blood cells to adequately supply oxygen to the tissue, can have many underlying causes. Treatment is based on hormones that stimulate the production of red blood cells but this has varying outcomes and it is difficult to estimate the effects treatment will have on a specific patient. Dr Doris H. Fuertinger at Fresenius Medical Care Deutschland is using a mathematical model to predict the causes of renal anaemia and to guide treatment for individual patients.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. 
What does this mean?
Share: You can copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
Adapt: You can change, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
Credit: You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made.
Related episodes
Dr. Serena Kuang | Inside the Kidney’s ‘Countercurrent’ Mystery: A New Model for Teaching and Studying Water Balance
Our kidneys filter blood to remove waste and can regulate water balance. We’ve all experienced that when we’re thirsty urine becomes concentrated, signalling us to drink more water. When we drink excess water, we urinate more frequently, and the urine is diluted. The kidneys’ ability to concentrate or dilute urine according to our body’s need relies on countercurrent multiplication (or CCM), a complex process that generates a salt concentration gradient in the kidney. However, CCM is challenging to teach and understand. Dr. Serena Kuang, a researcher and educator at Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine, has developed a more understandable CCM model and clears up errors in existing explanations making CCM easier to understand and teach.
Dr Neil Cunnigham | The Heart of the Matter: How Simulation Reflects Clinical Stress in Critical Care Training
In the high-stakes world of critical care, medical professionals are frequently called upon to perform life-saving procedures under intense pressure. Among these, airway intubation stands out as one of the most critical and technically demanding tasks. This procedure, which involves inserting a tube into a patient’s airway to ensure that they can breathe, is often performed in emergency situations where seconds count. The ability to intubate swiftly and accurately can mean the difference between life and death. However, this task is also fraught with stress, particularly for trainees who are still developing their skills. To better understand how these trainees cope with the stress of intubation, Dr Neil Cunningham of the University of Melbourne and colleagues conducted a groundbreaking study comparing physiological stress responses in simulated and clinical environments. Their findings offer valuable insights into the effectiveness of simulation-based training, which has become a cornerstone of medical education.
Dr. Ivy Razmus | Reducing Pressure Injuries in Hospitalized Children and Babies
The development of pressure injuries in hospital patients is a regular occurrence, and certain areas of the body are more susceptible. Although there is abundant research on pressure injuries in adult patients, studies relating to infant and child patients are lacking. Dr. Ivy Razmus at the University of Detroit Mercy has conducted extensive research on the prevention of pressure injuries in patients under the age of 12 years. She highlights the crucial role of advanced practice nurses in managing this widespread problem.
Pulque: The Ancient Drink That Could Shape the Future of Health
Pulque, an ancient Mexican beverage, is making waves in the scientific community—not just as a cultural relic, but as a potential health-boosting powerhouse. A team of researchers, including Prof. Rogelio Valadez-Blanco, Dr. Yesica Ruiz-Ramírez, and Prof. Paula Guadarrama-Mendoza, from Universidad Tecnológica de La Mixteca, has been investigating the hidden potential of the bacteria found in this traditional drink. Their findings suggest that pulque’s naturally occurring lactic acid bacteria could play a key role in promoting gut health and even combating harmful pathogens that cause foodborne illnesses.
Increase the impact of your research
• Good science communication helps people make informed decisions and motivates them to take appropriate and affirmative action.
• Good science communication encourages everyday people to be scientifically literate so that they can analyse the integrity and legitimacy of information.
• Good science communication encourages people into STEM-related fields of study and employment.
• Good public science communication fosters a community around research that includes both members of the public, policymakers and scientists.
• In a recent survey, 75% of people suggested they would prefer to listen to an interesting story than read it.

Step 1 Upload your science paper
Step 2 SciPod script written
Step 3 Voice audio recorded
Step 4 SciPod published