BEST in CLASS: Improving Interactions Between Teachers and Students – Drs Maureen Conroy and Kevin Sutherland
Jun 15, 2018education & training
Young students who exhibit problematic behaviours in school often fail to fully benefit from their educational experiences and can have adjustment problems later in life. Dr Maureen Conroy at the University of Florida and Dr Kevin Sutherland at Virginia Commonwealth University have been developing a classroom-based intervention model called BEST in CLASS, designed to improve how teachers and young children with chronic behavioural problems interact with each other.

You may also like …

Dr. Adeniyi Charles Adeola | The Genetic Blueprint of Nigerian Animals: How Genetics Research is Transforming Nigerian Wildlife and Farming
Across the varied and diverse landscapes that make up the Nigerian countryside, animals, both wild and domesticated, are more than merely an agricultural commodity or source of food; they are an integral part of local cultures, natural biodiversity, and represent an ecological treasure trove. Local wildlife and agricultural livestock help to sustain the livelihoods of millions. However, beyond this, Nigerian animals hold secrets within their genetic code that could, when revealed, help to prevent diseases, aid conservation efforts and enhance agricultural productivity. Leading the efforts to uncover useful and interesting genetic phenomena in these animals is Dr. Adeniyi Charles Adeola of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, who explores the genetic blueprints of Nigerian animals in his pioneering research. From investigating the population dynamics of grasscutters to tackling the genetic roots of prion diseases, Dr. Adeniyi Charles Adeola’s work illuminates both challenges and solutions that impact food security, agriculture, and biodiversity in Nigeria, and far beyond.

Professor Magnus S. Magnusson | The surprising similarities between the structures of human cells and societies
Research by Professor Magnus S. Magnusson at the University of Iceland demonstrates surprising similarities between the organization of cellular protein networks and of human societies. He reveals how the invention of writing and, very recently, general education, transformed human civilization in ways that mirror ancient biological developments and emphasises how this makes humans unique.
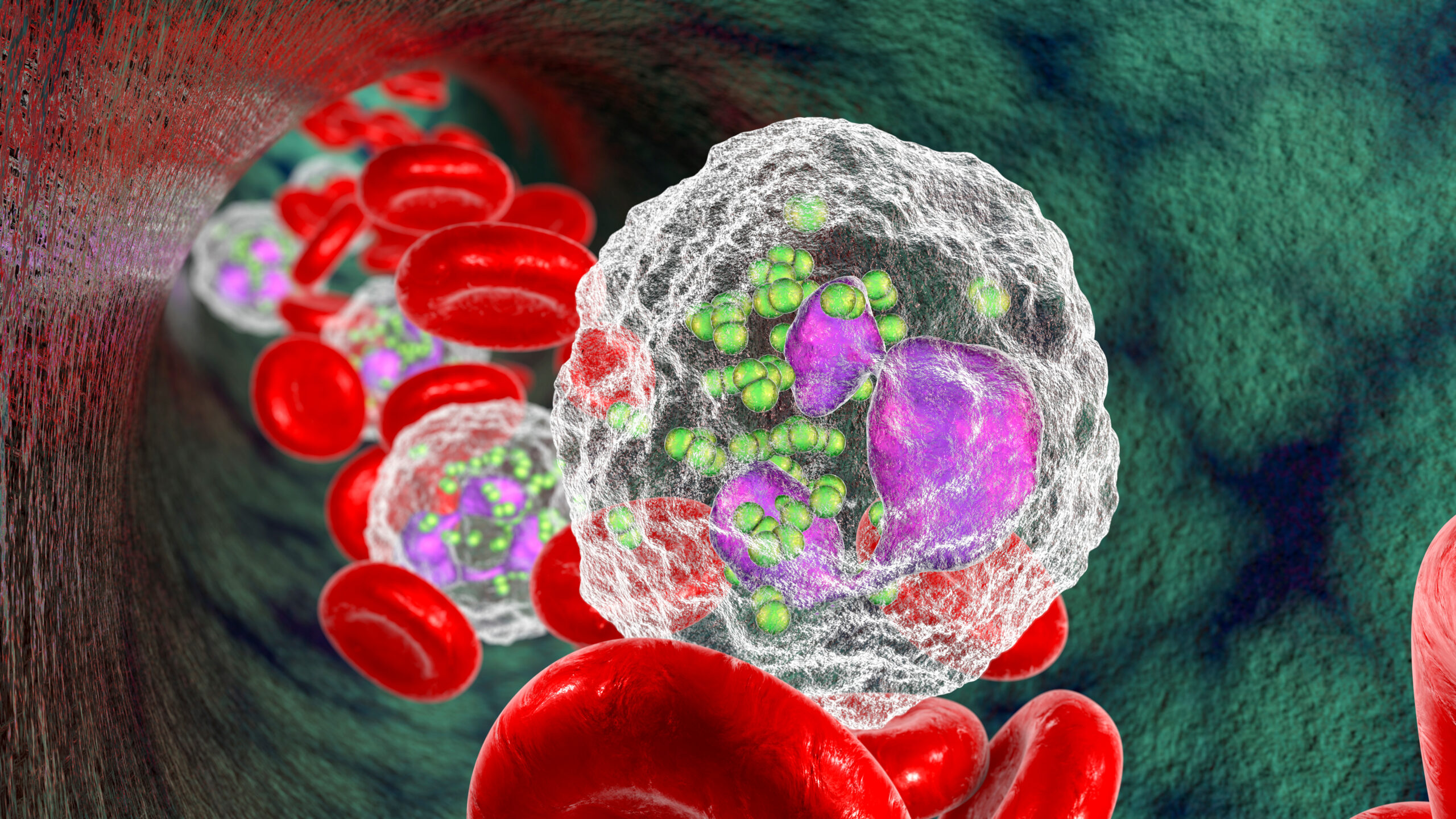
Dr. Roberta Martinelli | Sepsis and the Silent Battle Within: Neutrophils’ Role in Sepsis-Related Complications
Sepsis is a critical illness that begins with a simple infection and degenerates into a severe and dysregulated immune response that affects the whole body. This significant immune reaction typically causes widespread inflammation and can progress very rapidly. This can result in serious damage to tissues and organs, potentially leading to organ failure and death. Despite the severity of sepsis and its frequent poor prognosis, effective treatments are still elusive, and many sepsis patients remain at high risk of death and serious complications. Part of the issue is the complex cascade of cellular and biochemical events that underlie sepsis, which has made it difficult to obtain a comprehensive overview of the illness from which to design an effective treatment. Dr. Roberta Martinelli, Executive Director of Stromal Immunology and Early Discovery, Discovery Immunology, Merck, and colleagues, have published a study in the journal iScience which reveals new insights into the complex biological milieu underlying sepsis, and uncovers pathways and potential treatment targets that could change how we diagnose and treat this life-threatening illness.
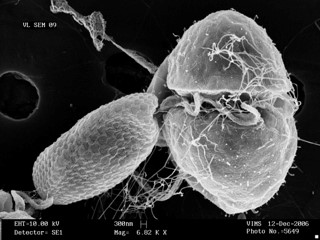
Dr. Allen Place | Small but Deadly: The Tale of K. veneficum
The oceans, huge and brimming with diverse lifeforms, pose no less a struggle for survival for their inhabitants than that faced by creatures on dry land. Evolution has furnished marine organisms with huge array of defensive, and indeed, offensive adaptations to help them to thrive in this battleground. Among the organisms who live and compete in the ocean are dinoflagellates. These are small, single-celled creatures that are an important component of plankton found in marine ecosystems. Despite their tiny size, dinoflagellates such as Karlodinium veneficum can wield potent biochemical weaponry that gives them an edge against other competing organisms. Decades since the discovery of the toxic properties of Karlodinium veneficum, researchers such as Dr. Allen Place of the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Sciences, and his colleagues, have begun to unravel the secrets of its potent toxins, called karlotoxins. Their findings offer fascinating insights into the interactions of marine life and the weapons they adopt to capture prey and deter predators.
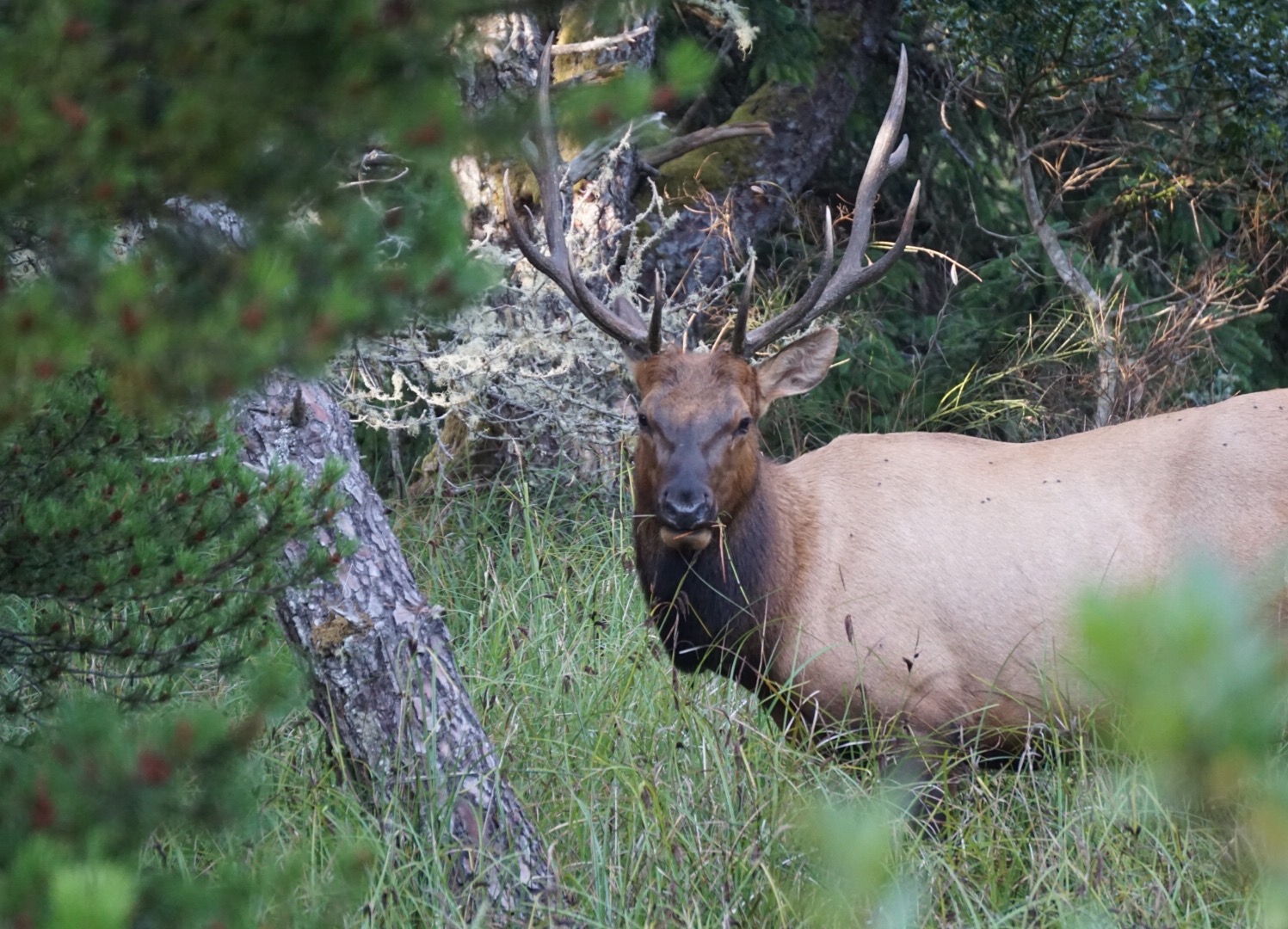

Dr. Andrea Grindeland | The Tiny Heroes That Could Save Deer and Elk from Chronic Wasting Disease
It’s not difficult to picture a lush forest landscape populated with majestic deer and elk, long admired for their prowess and strength. Now, imagine that same scene, but instead of healthy and happy animals browsing a forest ecosystem, we see creatures that are thin and disoriented, that struggle to run or even stand, with halting and confused movements that are pitiable and distressing to watch. This is the harsh reality of Chronic Wasting Disease, an illness that currently has no cure and that threatens such wildlife around the world. Part of the challenge with Chronic Wasting Disease is the difficulty in studying it reliably in wildlife. The disease has subtle signs at an early stage, and it is difficult to obtain robust and reproducible data from large, wild animals who often live in remote and poorly accessible forest ecosystems. Consequently, researchers have turned to an unlikely but powerful ally, the tiny laboratory mouse, to model and study the disease under laboratory conditions. Dr. Andrea Grindeland of the McLaughlin Research Institute, and her colleagues, have authored a review of the existing mouse models of Chronic Wasting Disease. These tiny creatures have been engineered to mimic the biology of cervids, such as deer and elk, and are providing crucial insights into how Chronic Wasting Disease evolves, is transmitted, and how it might one day be controlled or even eradicated.
Dr. Qiang Wang | Fishing for Findings: Uncovering the Genetics of Hearing Loss
Our hearing is amongst our most profound senses, connecting us to the surrounding world through sound. However, this connection is diminished or absent altogether in millions of people around the world because of hearing loss. Hearing loss is a common sensory disorder and is often hereditary. The condition can be caused by complex genetic factors, and so far, researchers have linked over 150 genes to hearing impairment. Now, a new collaborative study led by Dr. Qiang Wang of the South China University of Technology, Dr. Tao Cai from the National Institute of Health, and Dr. Yuan Li from the China-Japan Friendship Hospital in Beijing, has uncovered a new genetic clue, a mutation in the OXR1 gene, that could upend our understanding of hereditary hearing loss, and the eventual treatments that we develop to combat it.

Dr. Sarallah Rezazadeh | Unlocking the Secrets of Aging: How Stem Cells Hold the Key to Vitality
Aging is a tale written by the cells in our bodies, although some cell types play a bigger role than others. At the crux of this story is an intriguing protagonist: the stem cell. These master builders, which can differentiate into any cell type, thereby helping to replace diseased or worn-out tissues, are essential for tissue repair and in maintaining health into old age. But as we get older, the capabilities of stem cells gradually diminish, which is known as stem cell exhaustion and is a key facet of aging itself. Stem cell exhaustion plays a role in a large number of age-related diseases, meaning that it could be a crucial research target in developing new treatments and techniques to help us age well. A Research Topic in the open-access journal Frontiers in Aging has been curated by Dr. Sarallah Rezazadeh of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and Professor Georgina May Ellison-Hughes of King’s College London. The Topic collects groundbreaking studies into stem cell exhaustion under one open-access roof, exploring the detailed mechanisms underlying the phenomenon and establishing the field in a wider context to identify promising therapeutic approaches for those later in life.
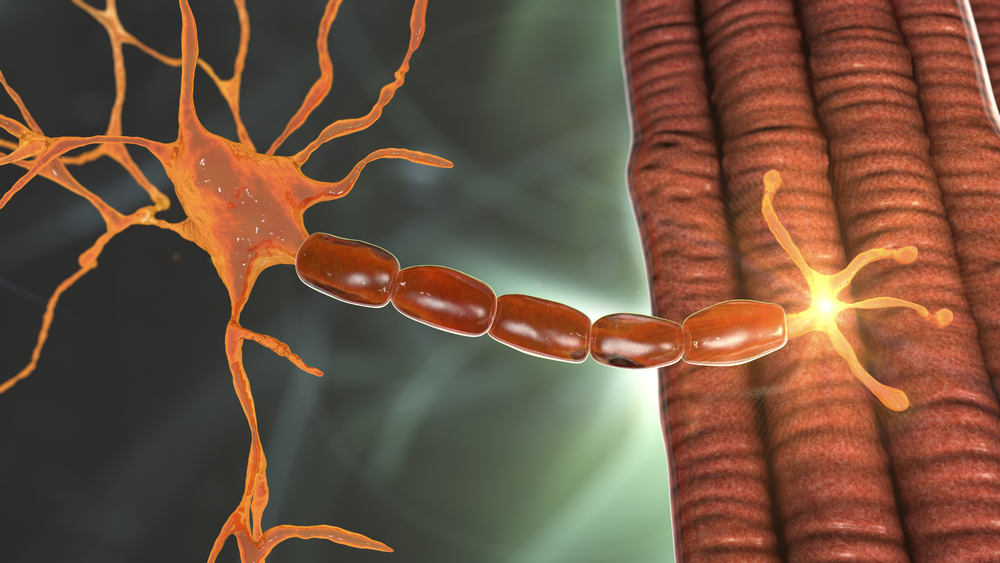
Charles Frison-Roche | The Hidden Architects of Movement: The Role of MBNL Proteins in Movement
Researchers have made a significant advancement in understanding an important component of the nervous system: the neuromuscular junction, a crucial connection between nerves and muscles. A recent study performed by Charles Frison-Roche of the Center of Research in Myology in the Sorbonne University, Paris, and colleagues, reveals the role of proteins known as Muscleblind-like proteins, or MBNL proteins for short, which help to regulate motor coordination by helping to maintain neuromuscular junction stability. This discovery is potentially very useful, as loss-of-function of MBNL proteins is a hallmark of a genetic condition called Myotonic Dystrophy type 1 (or DM1 for short). DM1 disrupts muscle control, leading to muscle weakness, problems with balance, and other symptoms that can get progressively worse over time. MBNL proteins, and their role in the neuromuscular junction, may represent new treatment targets in DM1.
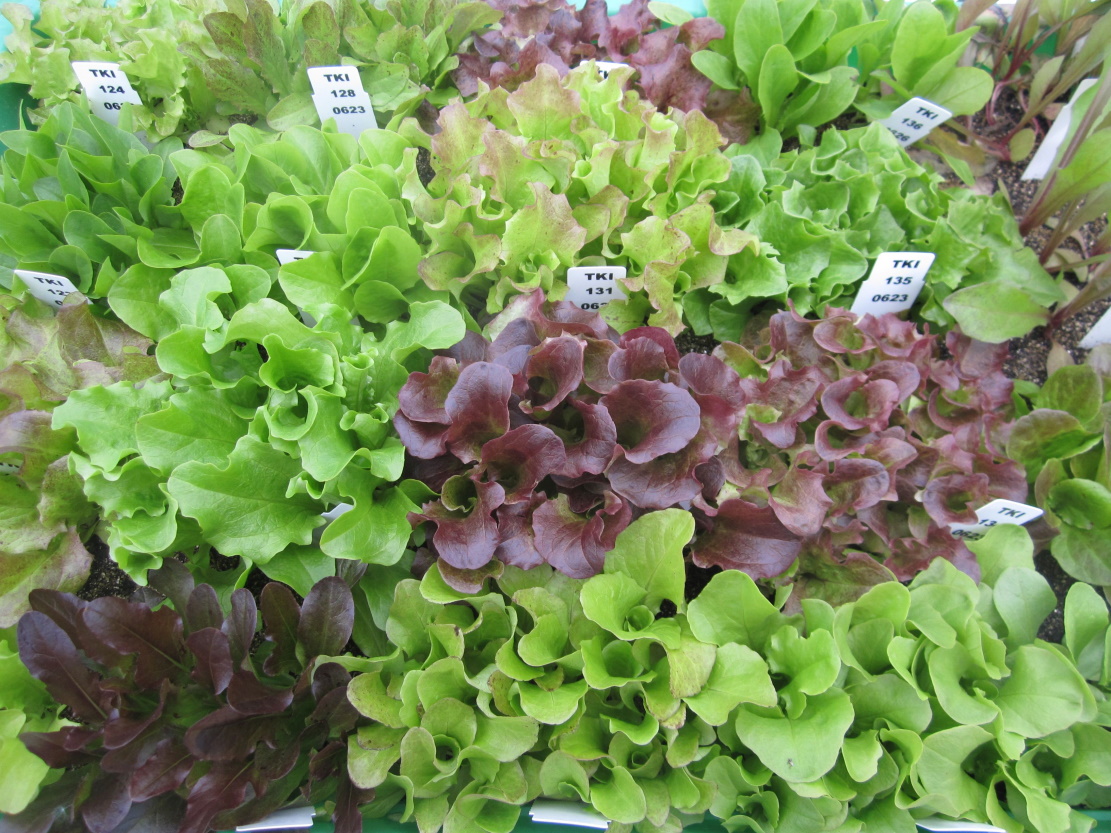

Dr Sandra Goritschnig – Dr Pasquale Tripodi | The Science of Greens: Using Genetic Insights to Cultivate Better, Stronger Lettuce
In recent years, rapid advancements in techniques for genetic analysis and manipulation have enhanced our potential to understand and improve crop diversity. An innovative project led by Dr. Pasquale Tripodi of the Italian Council for Agricultural Research and Economics and Dr Sandra Goritschnig of the European Cooperative Programme for Plant Genetic Resources marks a significant advance in the study of lettuce genetics. Their recently published research platforms a highly sophisticated technique to analyse genetic diversity within lettuces called Single Primer Enrichment Technology, or SPET for short. This approach provides a highly detailed view of lettuce genetics and also has significant implications for agricultural resilience and crop selection and breeding.
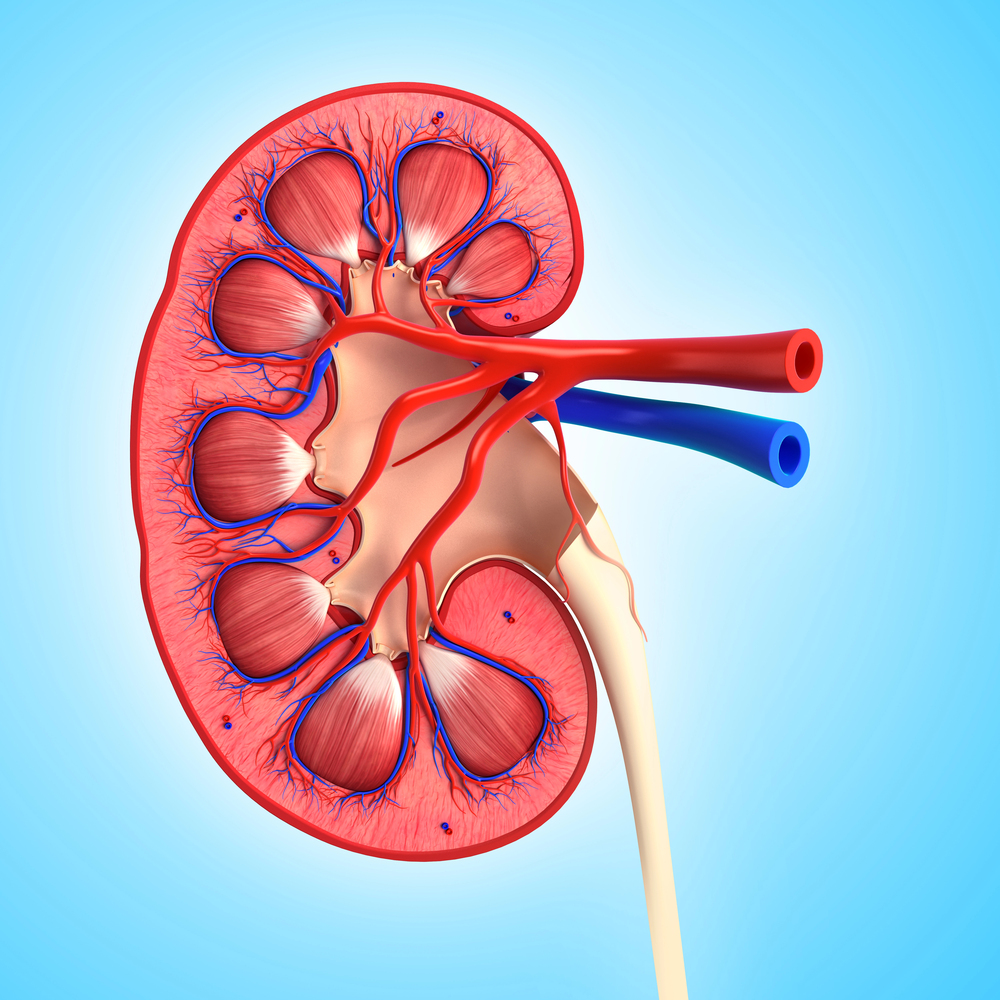
Dr. Serena Kuang | Inside the Kidney’s ‘Countercurrent’ Mystery: A New Model for Teaching and Studying Water Balance
Our kidneys filter blood to remove waste and can regulate water balance. We’ve all experienced that when we’re thirsty urine becomes concentrated, signalling us to drink more water. When we drink excess water, we urinate more frequently, and the urine is diluted. The kidneys’ ability to concentrate or dilute urine according to our body’s need relies on countercurrent multiplication (or CCM), a complex process that generates a salt concentration gradient in the kidney. However, CCM is challenging to teach and understand. Dr. Serena Kuang, a researcher and educator at Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine, has developed a more understandable CCM model and clears up errors in existing explanations making CCM easier to understand and teach.










